Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 20451522
- PMCID: PMC4862867
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.054
Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background & aims: Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is an hepatic protein that plays a critical role in metabolism, stimulating fatty acid oxidation in liver and glucose uptake in fat. Systemic administration to obese rodents and diabetic monkeys leads to improved glucose homeostasis and weight loss. In rodents, FGF21 increases with fasting and consumption of a ketogenic diet (KD). In humans, FGF21 correlates with body mass index (BMI), but studies evaluating other parameters show inconsistent results. We examined FGF21 serum levels in lean and obese individuals and in response to dietary manipulation. We also evaluated FGF21 serum levels and liver messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
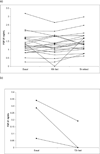
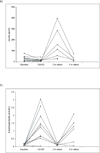
Methods: Serum FGF21 was measured after an overnight fast in individuals with BMI ranging from normal to obese. Volunteers fasted for 16 or 72 hours and then ate a standard meal. Another group consumed KD for 12 days. Serum FGF21 and hepatic mRNA expression were measured in obese individuals with NAFLD or NASH.
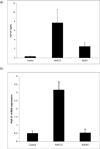
Results: There was a positive correlation between BMI and FGF21. There was no change in FGF21 in response to a short fast or KD. A nonstatistically significant fall in FGF21 levels was seen after a 72-hour fast. Hepatic FGF21 mRNA expression was significantly elevated in NAFLD, which correlated with a substantial increase in serum FGF21. In NASH, serum FGF21 but not liver mRNA was increased.
Conclusions: FGF21 correlates with BMI and may be a novel biomarker for NAFLD, but is not nutritionally regulated in humans.
Copyright (c) 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosures: There are no conflicts of interest to disclose for all authors.
Figures



References
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2000;1492(1):203–206. - PubMed
-
- Badman M, Pissios P, Kennedy A, et al. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARα and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5:426–437. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, et al. Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARα-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab. 2007;5(6):415–425. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy A, Pissios P, Otu H, et al. A high-fat, ketogenic diet induces a unique metabolic state in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292(6):E1724–E1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

