Inhibition of c-Jun kinase provides neuroprotection in a model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20451607
- PMCID: PMC2910136
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.04.015
Inhibition of c-Jun kinase provides neuroprotection in a model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
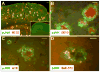
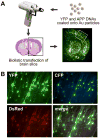
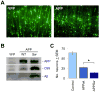
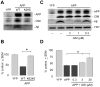
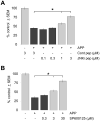
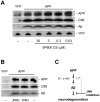
The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway potentially links together the three major pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD): development of amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and brain atrophy. As activation of the JNK pathway has been observed in amyloid models of AD in association with peri-plaque regions and neuritic dystrophy, as we confirm here for Tg2576/PS(M146L) transgenic mice, we directly tested whether JNK inhibition could provide neuroprotection in a novel brain slice model for amyloid precursor protein (APP)-induced neurodegeneration. We found that APP/amyloid beta (Abeta)-induced neurodegeneration is blocked by both small molecule and peptide inhibitors of JNK, and provide evidence that this neuroprotection occurs downstream of APP/Abeta production and processing. Our findings demonstrate that Abeta can induce neurodegeneration, at least in part, through the JNK pathway and suggest that inhibition of JNK may be of therapeutic utility in the treatment of AD.
Figures
References
-
- Barr RK, et al. Identification of the critical features of a small peptide inhibitor of JNK activity. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:10987–97. - PubMed
-
- Borsello T, et al. A peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase protects against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia. Nat Med. 2003;9:1180–6. - PubMed
-
- Brecht S, et al. Specific pathophysiological functions of JNK isoforms in the brain. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:363–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

