Mitochondria-centric activation induced cell death of cytolytic T lymphocytes and its implications for cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 20451638
- PMCID: PMC3870157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.04.074
Mitochondria-centric activation induced cell death of cytolytic T lymphocytes and its implications for cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
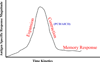
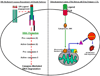
Premature death of the adoptively transferred cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL) by means of activation induced cell death (AICD) represents one of the major constraints in devising an effective anti-cancer immune intervention strategy. Understanding the mechanism of AICD is, therefore, critical for developing methods to interfere with this death process. Although the existing paradigm on AICD centers around the initiation of the cascade of events originating from the engagement of death receptors leading to the activation of effector caspases and eventually resulting in cell death, recent findings have questioned the universal role of caspases as the cell death executioners. We here review our current understanding of the contribution of caspase-dependent and caspase-independent death executioners in AICD of T cells. We will also discuss the involvement of mitochondria-centric death pathway in AICD of human tumor associated antigen-specific primary CTL and its implications in cancer immunotherapy.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- van der Bruggen P, Traversari C, Chomez P, et al. A gene encoding an antigen recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human melanoma. Science. 1991;254(5038):1643–1647. - PubMed
-
- Mukherji B, Chakraborty NG. Immunobiology and immunotherapy of melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 1995;7(2):175–184. - PubMed
-
- Nouri-Shirazi M, Banchereau J, Fay J, Palucka K. Dendritic cell based tumor vaccines. Immunol Lett. 2000;74(1):5–10. - PubMed
-
- Terando AM, Faries MB, Morton DL. Vaccine therapy for melanoma: Current status and future directions. Vaccine. 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

