Human bone marrow stem cell-encapsulating calcium phosphate scaffolds for bone repair
- PMID: 20451676
- PMCID: PMC2994102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.04.029
Human bone marrow stem cell-encapsulating calcium phosphate scaffolds for bone repair
Abstract
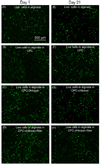
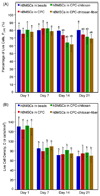
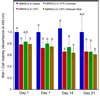
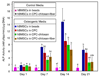
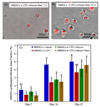
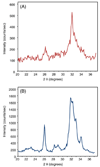
Due to its injectability and excellent osteoconductivity, calcium phosphate cement (CPC) is highly promising for orthopedic applications. However, a literature search revealed no report on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (hBMSC) encapsulation in CPC for bone tissue engineering. The aim of this study was to encapsulate hBMSCs in alginate hydrogel beads and then incorporate them into CPC, CPC-chitosan and CPC-chitosan-fiber scaffolds. Chitosan and degradable fibers were used to mechanically reinforce the scaffolds. After 21 days, that the percentage of live cells and the cell density of hBMSCs inside CPC-based constructs matched those in alginate without CPC, indicating that the CPC setting reaction did not harm the hBMSCs. Alkaline phosphate activity increased by 8-fold after 14 days. Mineral staining, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction confirmed that apatitic mineral was deposited by the cells. The amount of hBMSC-synthesized mineral in CPC-chitosan-fiber matched that in CPC without chitosan and fibers. Hence, adding chitosan and fibers, which reinforced the CPC, did not compromise hBMSC osteodifferentiation and mineral synthesis. In conclusion, hBMSCs were encapsulated in CPC and CPC-chitosan-fiber scaffolds for the first time. The encapsulated cells remained viable, osteodifferentiated and synthesized bone minerals. These self-setting, hBMSC-encapsulating CPC-based constructs may be promising for bone tissue engineering applications.
2010. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Phillips JH, Forrest CR, Gruss JS. Current concepts in the use of bone grafts in facial fractures. Basic science considerations. Clin Plast Surg. 1992;19:41–58. - PubMed
-
- Salgado AJ, Coutinho OP, Reis RL. Bone tissue engineering: state of the art and future trends. Macromol Biosci. 2004;4:743–765. - PubMed
-
- Shanti RM, Li WJ, Nesti LJ, Wang X, Tuan RS. Adult mesenchymal stem cells: biological properties, characteristics, and applications in maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:1640–1647. - PubMed
-
- Mao JJ. Stem cells and dentistry. J Dent Hyg. 2009;83:173–174. - PubMed
-
- Connelly JT, Garcia AJ, Levenston ME. Inhibition of in vitro chondrogenesis in RGD-modified three-dimensional alginate gels. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1071–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

