Epigenetic regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 governs neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation
- PMID: 20452318
- PMCID: PMC2867837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.02.017
Epigenetic regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 governs neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation
Abstract
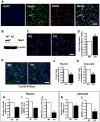
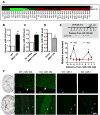
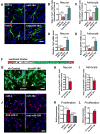
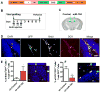
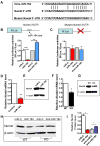
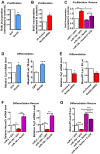
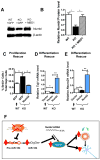
Methyl-CpG binding protein 1 (MBD1) regulates gene expression via a DNA methylation-mediated epigenetic mechanism. We have previously demonstrated that MBD1 deficiency impairs adult neural stem/progenitor cell (aNSC) differentiation and neurogenesis, but the underlying mechanism was unclear. Here, we show that MBD1 regulates the expression of several microRNAs in aNSCs and, specifically, that miR-184 is directly repressed by MBD1. High levels of miR-184 promoted proliferation but inhibited differentiation of aNSCs, whereas inhibition of miR-184 rescued the phenotypes associated with MBD1 deficiency. We further found that miR-184 regulates the expression of Numblike (Numbl), a known regulator of brain development, by binding to the 3'-UTR of Numbl mRNA and affecting its translation. Expression of exogenous Numbl could rescue the aNSC defects that result from either miR-184 overexpression or MBD1 deficiency. Therefore, MBD1, miR-184, and Numbl form a regulatory network that helps control the balance between proliferation and differentiation of aNSCs.
Figures
References
-
- Adams BD, Furneaux H, White BA. The micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and represses ERalpha messenger RNA and protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:1132–1147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

