Yorkie: the final destination of Hippo signaling
- PMID: 20452772
- PMCID: PMC2919348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.04.005
Yorkie: the final destination of Hippo signaling
Abstract
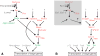
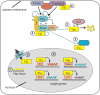
The Hippo signaling pathway is a key regulator of growth during animal development, whereas loss of normal Hippo pathway activity is associated with a wide range of cancers. Hippo signaling represses growth by inhibiting the activity of a transcriptional co-activator protein, known as Yorkie in Drosophila and Yap in vertebrates. In the 5 years since the first report linking Yorkie to Hippo signaling, intense interest in this pathway has led to rapid increases in our understanding of the action and regulation of Yorkie/Yap, which we review here. These studies have also emphasized the complexity of Yorkie/Yap regulation, including multiple, distinct mechanisms for repressing its transcriptional activity, and multiple DNA-binding partner proteins that can direct Yorkie to distinct downstream target genes.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Badouel C, et al. Herding Hippos: regulating growth in flies and man. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:837–843. - PubMed
-
- Reddy BV, Irvine KD. The Fat and Warts signaling pathways: new insights into their regulation, mechanism and conservation. Development. 2008;135:2827–2838. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, et al. The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell. 2005;122:421–434. - PubMed
-
- Justice RW, et al. The Drosophila tumor suppressor gene warts encodes a homolog of human myotonic dystrophy kinase and is required for the control of cell shape and proliferation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:534–546. - PubMed
-
- Xu T, et al. Identifying tumor suppressors in genetic mosaics: the Drosophila lats gene encodes a putative protein kinase. Development. 1995;121:1053–1063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

