The chemical biology of new drugs in the development for tuberculosis
- PMID: 20452813
- PMCID: PMC2918717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.04.008
The chemical biology of new drugs in the development for tuberculosis
Abstract
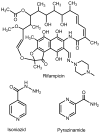
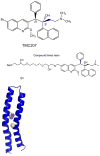
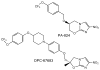
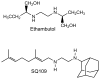
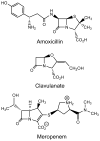
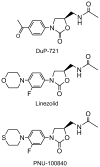
With the worldwide emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), there are serious concerns about the continued ability to contain this disease. We discuss the most promising new drugs in late-stage development that might be useful in treating MDR and XDR forms of the disease. These agents have novel mechanisms of action that are not targeted by the standard drugs used presently to treat susceptible strains.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Tsukamura M. A comparison of the time of in vivo resistance development of tubercle bacilli to rifampicin, kanamycin, ethionamide, lividomycin, and enviomycin (tuberactinomycin-N) in patients with chronic cavitary tuberculosis (author’s transl) Kekkaku. 1978;53:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Mitchison DA. The diagnosis and therapy of tuberculosis during the past 100 years. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:699–706. - PubMed
-
- Fox W, Mitchison DA. Short-course chemotherapy for tuberculosis. Lancet. 1976;2:1349–1350. An authoritative history and discussion of the development of the multi-drug chemotherapy currently used in the treatment of Tuberculosis. - PubMed
-
- Neff M. ATS, CDC, and IDSA update recommendations on the treatment of tuberculosis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68:1854, 1857–1858, 1861–1852. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Mitchison D. The curious characteristics of pyrazinamide: a review. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2003;7:6–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

