Genetic control of the inflammatory T-cell response in regulatory T-cell deficient scurfy mice
- PMID: 20452830
- PMCID: PMC2916692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2010.04.004
Genetic control of the inflammatory T-cell response in regulatory T-cell deficient scurfy mice
Abstract
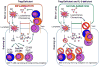
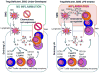
IPEX (Immunodysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked) syndrome is a rare, recessive disorder in patients with mutations in the foxp3 gene, the normal expression of which is required for the generation of functional regulatory T-cells. Scurfy mice also bear a mutation in the foxp3, and like IPEX patients, spontaneously develop multi-organ inflammation. As reviewed herein, breeding immune response genes into Scurfy mice has provided useful insight into how the inflammatory T-cell response is regulated in the absence of regulatory T-cells and post regulatory T-cell checkpoint. Of particular interest are those that preferentially affect the inflammatory T-cell response in an "apparent" organ-specific manner, implying that specific mechanisms of control exist for individual organs during multi-organ inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory T-cell dysfunction induces autoantibodies to bullous pemphigoid antigens in mice and human subjects.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Dec;142(6):1818-1830.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Apr 26. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29704593
-
Anti-CD4 treatment inhibits autoimmunity in scurfy mice through the attenuation of co-stimulatory signals.J Autoimmun. 2014 May;50:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.08.010. Epub 2013 Sep 25. J Autoimmun. 2014. PMID: 24075450
-
IPEX and FOXP3: clinical and research perspectives.J Autoimmun. 2005;25 Suppl:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2005.04.008. Epub 2005 Oct 21. J Autoimmun. 2005. PMID: 16243487 Review.
-
Role of CD28 in fatal autoimmune disorder in scurfy mice.Blood. 2007 Aug 15;110(4):1199-206. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-054585. Epub 2007 Apr 26. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17463170 Free PMC article.
-
IPEX, FOXP3 and regulatory T-cells: a model for autoimmunity.Immunol Res. 2007;38(1-3):112-21. doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0022-2. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17917016 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-2: a two-faced master regulator of autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2011 Mar;36(2):91-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21282039 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in congenital diarrheal disorders.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011 Jun;13(3):257-64. doi: 10.1007/s11894-011-0188-6. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21494839 Review.
-
IL233, A Novel IL-2 and IL-33 Hybrid Cytokine, Ameliorates Renal Injury.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Sep;28(9):2681-2693. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016121272. Epub 2017 May 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28539382 Free PMC article.
-
IL-2-controlled expression of multiple T cell trafficking genes and Th2 cytokines in the regulatory T cell-deficient scurfy mice: implication to multiorgan inflammation and control of skin and lung inflammation.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 15;186(2):1268-78. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002677. Epub 2010 Dec 17. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21169543 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced autoimmunity associated with deletion of host CD73.Immunohorizons. 2025 Jan 23;9(1):vlae004. doi: 10.1093/immhor/vlae004. Immunohorizons. 2025. PMID: 39846845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wing K, Fehervari Z, Sakaguchi S. Emerging possibilities in the development and function of regulatory T cells. Int Immunol. 2006;18:991–1000. - PubMed
-
- Bluestone JA, Tang Q. How do CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control autoimmunity? Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:638–642. - PubMed
-
- Piccirillo CA, Shevach EM. Naturally-occurring CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells: central players in the arena of peripheral tolerance. Semin Immunol. 2004;16:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Khattri R, Cox T, Yasayko SA, Ramsdell F. An essential role for scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA, Paeper B, Clark LB, Yasayko SA, Wilkinson JE, Galas D, Ziegler SF, Ramsdell F. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet. 2001;27:68–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

