Prospective study comparing skin impedance with EEG parameters during the induction of anaesthesia with fentanyl and etomidate
- PMID: 20452883
- PMCID: PMC3352044
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-2-47
Prospective study comparing skin impedance with EEG parameters during the induction of anaesthesia with fentanyl and etomidate
Abstract
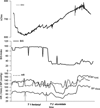
Objective: Sympathetic stimulation leads to a change in electrical skin impedance. So far it is unclear whether this effect can be used to measure the effects of anaesthetics during general anaesthesia. The aim of this prospective study is to determine the electrical skin impedance during induction of anaesthesia for coronary artery bypass surgery with fentanyl and etomidate.
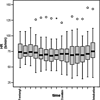
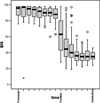
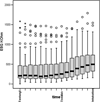
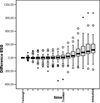
Methods: The electrical skin impedance was measured with the help of an electro-sympathicograph (ESG). In 47 patients scheduled for elective cardiac surgery, anaesthesia was induced with intravenous fentanyl 10 mug/kg and etomidate 0.3mg/kg. During induction, the ESG (Electrosympathicograph), BIS (Bispectral IndeX), BP (arterial blood pressure) and HR (heart rate) values of each patient were recorded every 20 seconds.The observation period from administration of fentanyl to intubation for surgery lasted 4 min. -
Results: The ESG recorded significant changes in the electrical skin impedance after administration of fentanyl and etomidate(p <0.05). During induction of anaesthesia, significant changes of BIS, HR and blood pressure were observed as well (p <0.05).
Conclusions: The electrical skin impedance measurement may be used to monitor the effects of anesthetics during general anaesthesia.
Figures
References
-
- Hess WC, Ohe A. Does ketamine/propofol anesthesia possess antiarrhythmogenic quality? A perioperative study in aortocoronary bypass patients. Eur J Med Res. 2001;6:543–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

