Nuclear functions of actin
- PMID: 20452941
- PMCID: PMC2845203
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000620
Nuclear functions of actin
Abstract
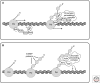
Actin participates in several essential processes in the cell nucleus. Even though the presence of actin in the nucleus was proposed more than 30 years ago, nuclear processes that require actin have been only recently identified. Actin is part of chromatin remodeling complexes; it is associated with the transcription machineries; it becomes incorporated into newly synthesized ribonucleoproteins; and it influences long-range chromatin organization. As in the cytoplasm, nuclear actin works in conjunction with different types of actin-binding proteins that regulate actin function and bridge interactions between actin and other nuclear components.
Figures
References
-
- Blessing CA, Ugrinova GT, Goodson HV 2004. Actin and ARPs: Action in the nucleus. Trends Cell Biol 14:435–442 - PubMed
-
- Cavellan E, Asp P, Percipalle P, Östlund Farrants AK 2006. The chromatin remodelling complex WSTF-SNF2 h interacts with several nuclear proteins in transcription. J Biol Chem 281:16264–16271 - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Shen X 2007. Nuclear actin and actin-related proteins in chromatin dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:326–330 - PubMed
-
- Chuang CH, Carpenter AE, Fuchsova B, Johnson T, de Lanerolle P, Belmont AS 2006. Long-range directional movement of an interphase chromosome site. Curr Biol 16:825–831 - PubMed
-
- Cisterna B, Malatesta M, Dieker J, Muller S, Prosperi E, Biggiogera M 2009. An active mechanism flanks and modulates the export of the small ribosomal subunits. Histochem Cell Biol 131:743–753 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
