Coordination of receptor signaling in multiple hematopoietic cell lineages by the adaptor protein SLP-76
- PMID: 20452948
- PMCID: PMC2845197
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002501
Coordination of receptor signaling in multiple hematopoietic cell lineages by the adaptor protein SLP-76
Abstract
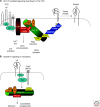
The adaptor protein SLP-76 is expressed in multiple hematopoietic lineages including T cells, platelets, and neutrophils. SLP-76 mediated signaling is dependent on its multiple protein interaction domains, as it creates a scaffold on which key signaling complexes are built. SLP-76 is critical for supporting signaling downstream of both immunoreceptors and integrins. The signaling molecules used both upstream and downstream of SLP-76 are similar among these receptors and across cell types; however, important differences exist. Appreciating how SLP-76 coordinates signal transduction across different cell and receptor types provides insights into the complex interplay of pathways critical for activation of cells of the immune system that are essential for host defense.
Figures

References
-
- Atherly LO, Lucas JA, Felices M, Yin CC, Reiner SL, Berg LJ 2006. The Tec family tyrosine kinases Itk and Rlk regulate the development of conventional CD8+ T cells. Immunity 25:79–91 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
