Pregnenolone sulfate and cortisol induce secretion of acyl-CoA-binding protein and its conversion into endozepines from astrocytes
- PMID: 20452969
- PMCID: PMC2898429
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105858
Pregnenolone sulfate and cortisol induce secretion of acyl-CoA-binding protein and its conversion into endozepines from astrocytes
Abstract
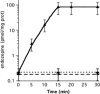
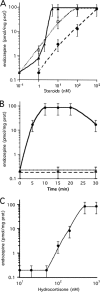
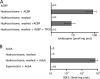
Acyl-CoA-binding protein (ACBP) functions both intracellularly as part of fatty acid metabolism and extracellularly as diazepam binding inhibitor, the precursor of endozepine peptides. Two of these peptides, ODN and TTN, bind to the GABA(A) receptor and modulate its sensitivity to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). We have found that depolarization of mouse primary astrocytes induces the rapid release and processing of ACBP to the active peptides. We previously showed that ODN can trigger the rapid sporulation of the social amoeba Dictyostelium. Using this bioassay, we now show that astrocytes release the endozepine peptides within 10 min of exposure to the steroids cortisol, pregnenolone, pregnenolone sulfate, or progesterone. ACBP lacks a signal sequence for secretion through the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi pathway and its secretion is not affected by addition of brefeldin A, a well known inhibitor of the classical secretion pathway, suggesting that it follows an unconventional pathway for secretion. Moreover, induction of autophagy by addition of rapamycin also resulted in rapid release of ACBP indicating that this protein uses components of the autophagy pathway for secretion. Following secretion, ACBP is proteolytically cleaved to the active neuropeptides by protease activity on the surface of astrocytes. Neurosteroids, such as pregnenolone sulfate, were previously shown to modulate the excitatory/inhibitory balance in brain through increased release of glutamate and decreased release of GABA. These effects of steroids in neurons will be reinforced by the release of endozepines from astrocytes shown here, and suggest an orchestrated astrocyte-neuron cross-talk that can affect a broad spectrum of behavioral functions.
Figures
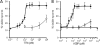
References
-
- Faergeman N. J., Wadum M., Feddersen S., Burton M., Kragelund B. B., Knudsen J. (2007) Mol. Cell. Biochem. 299, 55–65 - PubMed
-
- Knudsen J., Mandrup S., Rasmussen J. T., Andreasen P. H., Poulsen F., Kristiansen K. (1993) Mol. Cell. Biochem. 123, 129–138 - PubMed
-
- Guarneri P., Berkovich A., Guidotti A., Costa E. (1990) Neuropharmacology 29, 419–428 - PubMed
-
- Slobodyansky E., Guidotti A., Wambebe C., Berkovich A., Costa E. (1989) J. Neurochem. 53, 1276–1284 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

