Receptor-regulated interaction of activator of G-protein signaling-4 and Galphai
- PMID: 20452976
- PMCID: PMC2898320
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C109.088070
Receptor-regulated interaction of activator of G-protein signaling-4 and Galphai
Abstract
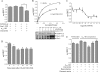
Activator of G-protein signaling-4 (AGS4), via its three G-protein regulatory motifs, is well positioned to modulate G-protein signal processing by virtue of its ability to bind Galpha(i)-GDP subunits free of Gbetagamma. Apart from initial observations on the biochemical activity of the G-protein regulatory motifs of AGS4, very little is known about the nature of the AGS4-G-protein interaction, how this interaction is regulated, or where the interaction takes place. As an initial approach to these questions, we evaluated the interaction of AGS4 with Galpha(i1) in living cells using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). AGS4 and Galpha(i1) reciprocally tagged with either Renilla luciferase (RLuc) or yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) demonstrated saturable, specific BRET signals. BRET signals observed between AGS4-RLuc and Galpha(i1)-YFP were reduced by G-protein-coupled receptor activation, and this agonist-induced reduction in BRET was blocked by pertussis toxin. In addition, specific BRET signals were observed for AGS4-RLuc and alpha(2)-adrenergic receptor-Venus, which were Galpha(i)-dependent and reduced by agonist, indicating that AGS4-Galpha(i) complexes are receptor-proximal. These data suggest that AGS4-Galpha(i) complexes directly couple to a G-protein-coupled receptor and may serve as substrates for agonist-induced G-protein activation.
Figures
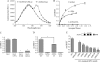

References
-
- Cao X., Cismowski M. J., Sato M., Blumer J. B., Lanier S. M. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 27567–27574 - PubMed
-
- Cismowski M. J., Takesono A., Ma C., Lizano J. S., Xie X., Fuernkranz H., Lanier S. M., Duzic E. (1999) Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 878–883 - PubMed
-
- Takesono A., Cismowski M. J., Ribas C., Bernard M., Chung P., Hazard S., 3rd, Duzic E., Lanier S. M. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33202–33205 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

