Rab3-interacting molecule gamma isoforms lacking the Rab3-binding domain induce long lasting currents but block neurotransmitter vesicle anchoring in voltage-dependent P/Q-type Ca2+ channels
- PMID: 20452978
- PMCID: PMC2898395
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101311
Rab3-interacting molecule gamma isoforms lacking the Rab3-binding domain induce long lasting currents but block neurotransmitter vesicle anchoring in voltage-dependent P/Q-type Ca2+ channels
Abstract
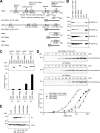
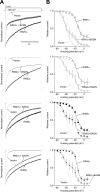
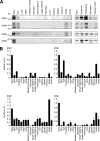
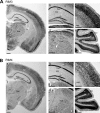
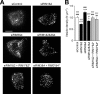
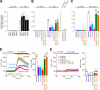
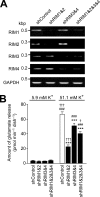
Assembly of voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels (VDCCs) with their associated proteins regulates the coupling of VDCCs with upstream and downstream cellular events. Among the four isoforms of the Rab3-interacting molecule (RIM1 to -4), we have previously reported that VDCC beta-subunits physically interact with the long alpha isoform of the presynaptic active zone scaffolding protein RIM1 (RIM1alpha) via its C terminus containing the C(2)B domain. This interaction cooperates with RIM1alpha-Rab3 interaction to support neurotransmitter exocytosis by anchoring vesicles in the vicinity of VDCCs and by maintaining depolarization-triggered Ca(2+) influx as a result of marked inhibition of voltage-dependent inactivation of VDCCs. However, physiological functions have not yet been elucidated for RIM3 and RIM4, which exist only as short gamma isoforms (gamma-RIMs), carrying the C-terminal C(2)B domain common to RIMs but not the Rab3-binding region and other structural motifs present in the alpha-RIMs, including RIM1alpha. Here, we demonstrate that gamma-RIMs also exert prominent suppression of VDCC inactivation via direct binding to beta-subunits. In the pheochromocytoma PC12 cells, this common functional feature allows native RIMs to enhance acetylcholine secretion, whereas gamma-RIMs are uniquely different from alpha-RIMs in blocking localization of neurotransmitter-containing vesicles near the plasma membrane. Gamma-RIMs as well as alpha-RIMs show wide distribution in central neurons, but knockdown of gamma-RIMs attenuated glutamate release to a lesser extent than that of alpha-RIMs in cultured cerebellar neurons. The results suggest that sustained Ca(2+) influx through suppression of VDCC inactivation by RIMs is a ubiquitous property of neurons, whereas the extent of vesicle anchoring to VDCCs at the plasma membrane may depend on the competition of alpha-RIMs with gamma-RIMs for VDCC beta-subunits.
Figures
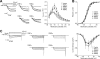


Similar articles
-
C-terminal splice variants of P/Q-type Ca2+ channel CaV2.1 α1 subunits are differentially regulated by Rab3-interacting molecule proteins.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 2;292(22):9365-9381. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778829. Epub 2017 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28377503 Free PMC article.
-
RIM1 confers sustained activity and neurotransmitter vesicle anchoring to presynaptic Ca2+ channels.Nat Neurosci. 2007 Jun;10(6):691-701. doi: 10.1038/nn1904. Epub 2007 May 13. Nat Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17496890 Free PMC article.
-
The RIM/NIM family of neuronal C2 domain proteins. Interactions with Rab3 and a new class of Src homology 3 domain proteins.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 30;275(26):20033-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M909008199. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10748113
-
Functional interactions between voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels and Rab3-interacting molecules (RIMs): new insights into stimulus-secretion coupling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Mar;1818(3):551-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.12.011. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22198390 Review.
-
RIM proteins and their role in synapse function.Biol Chem. 2010 Jun;391(6):599-606. doi: 10.1515/BC.2010.064. Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20370319 Review.
Cited by
-
RIM1 and RIM2 redundantly determine Ca2+ channel density and readily releasable pool size at a large hindbrain synapse.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Jan 1;113(1):255-63. doi: 10.1152/jn.00488.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25343783 Free PMC article.
-
Folic Acid Supplementation Promotes Hypomethylation in Both the Inflamed Colonic Mucosa and Colitis-Associated Dysplasia.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 27;15(11):2949. doi: 10.3390/cancers15112949. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296911 Free PMC article.
-
Functional coupling of Rab3-interacting molecule 1 (RIM1) and L-type Ca2+ channels in insulin release.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 6;286(18):15757-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187757. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21402706 Free PMC article.
-
Gene knockout of RNA binding motif 5 in the brain alters RIMS2 protein homeostasis in the cerebellum and Hippocampus and exacerbates behavioral deficits after a TBI in mice.Exp Neurol. 2024 Apr;374:114690. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114690. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38218585 Free PMC article.
-
Active zone protein Bassoon co-localizes with presynaptic calcium channel, modifies channel function, and recovers from aging related loss by exercise.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038029. Epub 2012 Jun 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

