TRIF modulates TLR5-dependent responses by inducing proteolytic degradation of TLR5
- PMID: 20452988
- PMCID: PMC2898416
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115022
TRIF modulates TLR5-dependent responses by inducing proteolytic degradation of TLR5
Abstract
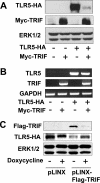
Proteolytic modification of pattern recognition receptors and their signaling adaptor molecules has recently emerged as an essential cellular event to regulate immune and inflammatory responses. Here we show that the TIR domain containing adaptor-inducing interferon-beta (TRIF), an adaptor molecule mediating TLR3 signaling and MyD88-independent signaling of TLR4, plays an inhibitory role in TLR5-elicited responses by inducing proteolytic degradation of TLR5. TRIF overexpression in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) and human colonic epithelial (NCM460) cells abolishes the cellular protein level of TLR5, whereas it does not alter TLR5 mRNA level. Thus, TRIF overexpression dramatically suppresses flagellin/TLR5-deriven NFkappaB activation in NCM460 cells. TRIF-induced TLR5 protein degradation is completely inhibited in the presence of pan-caspase inhibitor (benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone), whereas several specific inhibitors against cathepsin B, reactive oxygen species, or ubiquitin-mediated proteasome activity fail to suppress this degradation. These results indicate that TRIF-induced caspase activity causes TLR5 protein degradation. In addition, we identify that the C terminus of TRIF and extracellular domain of TLR5 are required for TRIF-induced TLR5 degradation. Furthermore, TRIF-induced proteolytic degradation is extended to TLR3, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, and TLR10, whereas the cellular level of TLR1, TLR2, and TLR4 is not affected by TRIF overexpression. These results suggest that, in addition to mediating TLR3- or TLR4-induced signaling as an adaptor molecule, TRIF can participate in proteolytic modification of certain members of TLRs to modulate the functionality of TLRs at post-translational level. Collectively, our findings propose a potential inhibitory role of TRIF at least in regulating host-microbial communication via TLR5 in colonic epithelial cells.
Figures







References
-
- Palm N. W., Medzhitov R. (2009) Immunol. Rev. 227, 221–233 - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R., Preston-Hurlburt P., Kopp E., Stadlen A., Chen C., Ghosh S., Janeway C. A., Jr. (1998) Mol. Cell 2, 253–258 - PubMed
-
- Oshiumi H., Matsumoto M., Funami K., Akazawa T., Seya T. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4, 161–167 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2008) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1143, 1–20 - PubMed
-
- Kenny E. F., O'Neill L. A. (2008) Cytokine 43, 342–349 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

