A screen of chemical modifications identifies position-specific modification by UNA to most potently reduce siRNA off-target effects
- PMID: 20453030
- PMCID: PMC2943616
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq341
A screen of chemical modifications identifies position-specific modification by UNA to most potently reduce siRNA off-target effects
Abstract
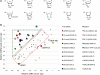
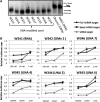
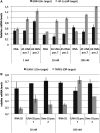
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are now established as the preferred tool to inhibit gene function in mammalian cells yet trigger unintended gene silencing due to their inherent miRNA-like behavior. Such off-target effects are primarily mediated by the sequence-specific interaction between the siRNA seed regions (position 2-8 of either siRNA strand counting from the 5'-end) and complementary sequences in the 3'UTR of (off-) targets. It was previously shown that chemical modification of siRNAs can reduce off-targeting but only very few modifications have been tested leaving more to be identified. Here we developed a luciferase reporter-based assay suitable to monitor siRNA off-targeting in a high throughput manner using stable cell lines. We investigated the impact of chemically modifying single nucleotide positions within the siRNA seed on siRNA function and off-targeting using 10 different types of chemical modifications, three different target sequences and three siRNA concentrations. We found several differently modified siRNAs to exercise reduced off-targeting yet incorporation of the strongly destabilizing unlocked nucleic acid (UNA) modification into position 7 of the siRNA most potently reduced off-targeting for all tested sequences. Notably, such position-specific destabilization of siRNA-target interactions did not significantly reduce siRNA potency and is therefore well suited for future siRNA designs especially for applications in vivo where siRNA concentrations, expectedly, will be low.
Figures



References
-
- Dykxhoorn DM, Lieberman J. RUNNING INTERFERENCE: prospects and obstacles to using small interfering RNAs as small molecule drugs. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006;8:377–402. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Matranga C, Tomari Y, Shin C, Bartel DP, Zamore PD. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell. 2005;123:607–620. - PubMed
-
- Rand TA, Petersen S, Du F, Wang X. Argonaute2 cleaves the anti-guide strand of siRNA during RISC activation. Cell. 2005;123:621–629. - PubMed
-
- Hornung V, Guenthner-Biller M, Bourquin C, Ablasser A, Schlee M, Uematsu S, Noronha A, Manoharan M, Akira S, de Fougerolles A, et al. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-alpha by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nat. Med. 2005;11:263–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

