Oligomeric sensor kinase DcuS in the membrane of Escherichia coli and in proteoliposomes: chemical cross-linking and FRET spectroscopy
- PMID: 20453099
- PMCID: PMC2897680
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00082-10
Oligomeric sensor kinase DcuS in the membrane of Escherichia coli and in proteoliposomes: chemical cross-linking and FRET spectroscopy
Abstract
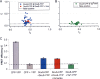
DcuS is the membrane-integral sensor histidine kinase of the DcuSR two-component system in Escherichia coli that responds to extracellular C(4)-dicarboxylates. The oligomeric state of full-length DcuS was investigated in vitro and in living cells by chemical cross-linking and by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) spectroscopy. The FRET results were quantified by an improved method using background-free spectra of living cells for determining FRET efficiency (E) and donor fraction {f(D) = (donor)/[(donor) + (acceptor)]}. Functional fusions of cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) and yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) variants of green fluorescent protein to DcuS were used for in vivo FRET measurements. Based on noninteracting membrane proteins and perfectly interacting proteins (a CFP-YFP fusion), the results of FRET of cells coexpressing DcuS-CFP and DcuS-YFP were quantitatively evaluated. In living cells and after reconstitution of purified recombinant DcuS in proteoliposomes, DcuS was found as a dimer or higher oligomer, independent of the presence of an effector. Chemical cross-linking with disuccinimidyl suberate showed tetrameric, in addition to dimeric, DcuS in proteoliposomes and in membranes of bacteria, whereas purified DcuS in nondenaturing detergent was mainly monomeric. The presence and amount of tetrameric DcuS in vivo and in proteoliposomes was not dependent on the concentration of DcuS. Only membrane-embedded DcuS (present in the oligomeric state) is active in (auto)phosphorylation. Overall, the FRET and cross-linking data demonstrate the presence in living cells, in bacterial membranes, and in proteoliposomes of full-length DcuS protein in an oligomeric state, including a tetramer.
Figures


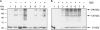


References
-
- Balannik, V., R. A. Lamb, and L. H. Pinto. 2008. The oligomeric state of the active BM2 ion channel protein of influenza B virus. J. Biol. Chem. 283:4895-4904. - PubMed
-
- Biener, E., M. Charlier, V. K. Ramanujan, N. Daniel, A. Eisenberg, C. Bjorbaek, B. Herman, A. Gertler, and J. Djiane. 2005. Quantitative FRET imaging of leptin receptor oligomerization kinetics in single cells. Biol. Cell 97:905-919. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principles of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

