Apparent PKA activity responds to intermittent hypoxia in bone cells: a redox pathway?
- PMID: 20453101
- PMCID: PMC2904137
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01073.2009
Apparent PKA activity responds to intermittent hypoxia in bone cells: a redox pathway?
Abstract
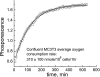
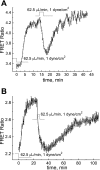
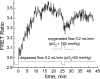
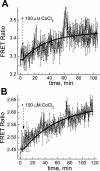
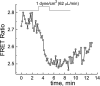
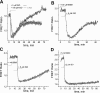
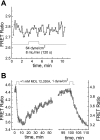
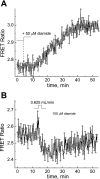
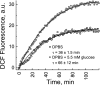
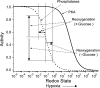
We studied hypoxia-induced dynamic changes in the balance between PKA and PKA-counteracting phosphatases in the microfluidic environment in single cells using picosecond fluorescence spectroscopy and intramolecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based sensors of PKA activity. First, we found that the apparent PKA activity in bone cells (MC3T3-E1 cells) and endothelial cells (bovine aortic endothelial cells) is rapidly and sensitively modulated by the level of O(2) in the media. When the O(2) concentration in the glucose-containing media was lowered due to O(2) consumption by the cells in the microfluidic chamber, the apparent PKA activity increases; the reoxygenation of cells under hypoxia leads to a rapid ( approximately 2 min) decrease of the apparent PKA activity. Second, lack of glucose in the media led to a lower apparent PKA activity and to a reversal of the response of the apparent PKA activity to hypoxia and reoxygenation. Third, the apparent PKA activity in cells under hypoxia was predominantly regulated via a cAMP-independent pathway since 1) changes in the cAMP level in the cells were not detected using a cAMP FRET sensor, 2) the decay of cAMP levels was too slow to account for the fast decrease in PKA activity levels in response to reoxygenation, and 3) the response of the apparent PKA activity due to hypoxia/reoxygenation was not affected by an adenylate cyclase inhibitor (MDL-12,330A) at 1 mM concentration. Fourth, the immediate onset of ROS accumulation in MC3T3-E1 cells subjected to hypoxia and the sensitivity of the apparent PKA activity to redox levels suggest that the apparent PKA activity change during hypoxia and reoxygenation in this study can be linked to a redox potential change in response to intermittent hypoxia through the regulation of activities of PKA-counteracting phosphatases such as protein phosphatase 1. Finally, our results suggest that the detection of PKA activity could be used to monitor responses of cells to hypoxia in real time.
Figures
Similar articles
-
cAMP/PKA antagonizes thrombin-induced inactivation of endothelial myosin light chain phosphatase: role of CPI-17.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Jul 15;87(2):375-84. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq065. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20202976
-
Oxidant activated soluble adenylate cyclase of Leishmania donovani regulates the cAMP-PKA signaling axis for its intra-macrophage survival during infection.J Cell Biochem. 2021 Oct;122(10):1413-1427. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30018. Epub 2021 Jun 8. J Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34101889
-
PKA-dependent activation of PDE3A and PDE4 and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase V/VI in smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002 Mar;282(3):C508-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00373.2001. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11832336
-
Heterologous sensitization of adenylate cyclase is protein kinase A-dependent in Cath.a differentiated (CAD)-D2L cells.J Neurochem. 2002 Sep;82(5):1087-96. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01033.x. J Neurochem. 2002. PMID: 12358756
-
PKA functions in metabolism and resistance to obesity: lessons from mouse and human studies.J Endocrinol. 2020 Sep;246(3):R51-R64. doi: 10.1530/JOE-20-0035. J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32485681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Hypoxia on the Expression of CXC Chemokines and CXC Chemokine Receptors-A Review of Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 15;22(2):843. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020843. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33467722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia. 4. Hypoxia and ion channel function.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):C951-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00512.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21178108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A kinase interacting protein (AKIP1) is a key regulator of cardiac stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 29;110(5):E387-96. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221670110. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23319652 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Excessive Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartic Acid Receptors in Neonatal Cardiac Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Intrauterine Hypoxia.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Mar 30;9:837142. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.837142. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35498024 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic and Cycling Hypoxia: Drivers of Cancer Chronic Inflammation through HIF-1 and NF-κB Activation: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10701. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen MD, Zhang J. Subcellular dynamics of protein kinase A activity visualized by FRET-based reporters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348: 716–721, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Archer SL, Michelakis ED, Thebaud B, Bonnet S, Moudgil R, Wu XC, Weir EK. A central role for oxygen-sensitive K+ channels and mitochondria in the specialized oxygen-sensing system. Novartis Found Symp 272: 157–171, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Beitner-Johnson D, Leibold J, Millhorn DE. Hypoxia regulates the cAMP- and Ca2+/calmodulin signaling systems in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 242: 61–66, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bolon ML, Ouellette Y, Li F, Tyml K. Abrupt reoxygenation following hypoxia reduces electrical coupling between endothelial cells of wild-type but not connexin40 null mice in oxidant- and PKA-dependent manner. FASEB J 19: 1725–1727, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Boo YC, Jo H. Flow-dependent regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase: role of protein kinases. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285: C499–C508, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

