Hydrogen production by the unicellular, diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. strain ATCC 51142 under conditions of continuous light
- PMID: 20453150
- PMCID: PMC2897434
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00146-10
Hydrogen production by the unicellular, diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. strain ATCC 51142 under conditions of continuous light
Abstract
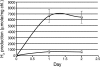
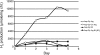
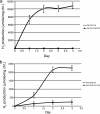
We report on the hydrogen production properties of the unicellular, diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. strain ATCC 51142. This organism has a versatile metabolism and can grow in the presence or absence of combined nitrogen and can grow photosynthetically or mixotrophically and heterotrophically in the presence of glycerol. The strain produces a bidirectional hydrogenase (encoded by the hox genes), an uptake hydrogenase (hupLS), and nitrogenase (nifHDK). We demonstrated hydrogen production by both the hydrogenase and the nitrogenase under appropriate metabolic conditions. The highest rates of hydrogen production were produced under nitrogen-fixing conditions when cells were grown and incubated under continuous light conditions, in either the presence or absence of glycerol. Under such nitrogen-fixing conditions, we have achieved rates of 300 micromol H(2)/mg chloramphenicol (Chl)/hr during the first 24 h of incubation. The levels of H(2) measured were dependent upon the incubation conditions, such as sparging with argon, which generated anaerobic conditions. We demonstrated that the same conditions led to high levels of H(2) production and N(2) fixation, indicating that low-oxygen conditions favor nitrogenase activity for both processes. The levels of hydrogen produced by the hydrogenase are much lower, typically 5 to 10 micromol H(2)/mg Chl/hr. Hydrogenase activity was dependent upon electron transport through photosystem II (PS II), whereas nitrogenase activity was more dependent on PS I, as well as on respiration. Although cells do not double under the incubation conditions when sparged with argon to provide a low-oxygen environment, the cells are metabolically active, and hydrogen production can be inhibited by the addition of chloramphenicol to inhibit protein synthesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Better living through cyanothece - unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacteria with highly versatile metabolic systems.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;675:275-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1528-3_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20532747
-
The uptake hydrogenase in the unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. strain PCC 7822 protects nitrogenase from oxygen toxicity.J Bacteriol. 2014 Feb;196(4):840-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01248-13. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24317398 Free PMC article.
-
Mixotrophic and photoheterotrophic metabolism in Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142 under continuous light.Microbiology (Reading). 2010 Aug;156(Pt 8):2566-2574. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.038232-0. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Microbiology (Reading). 2010. PMID: 20430816
-
[Hydrogen in metabolism of purple bacteria and prospects for practical applications].Mikrobiologiia. 2015 Jan-Feb;84(1):3-26. Mikrobiologiia. 2015. PMID: 25916143 Review. Russian.
-
H2 metabolism in photosynthetic bacteria and relationship to N2 fixation.Ann Microbiol (Paris). 1983 Jul-Aug;134B(1):115-35. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(83)80100-8. Ann Microbiol (Paris). 1983. PMID: 6139053 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic modelling of high biomass density cultivation and biohydrogen production in different scales of flat plate photobioreactors.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015 Dec;112(12):2429-38. doi: 10.1002/bit.25661. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015. PMID: 26041472 Free PMC article.
-
Dark fermentative hydrogen production and transcriptional analysis of genes involved in the unicellular halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica under nitrogen and potassium deprivation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 6;10:1028151. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1028151. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36686224 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Dynamics in Trichodesmium Colonies and Their Potential Role in Mineral Iron Acquisition.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 10;10:1565. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01565. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31354665 Free PMC article.
-
High rates of photobiological H2 production by a cyanobacterium under aerobic conditions.Nat Commun. 2010;1:139. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1139. Nat Commun. 2010. PMID: 21266989
-
Genome-scale modeling of light-driven reductant partitioning and carbon fluxes in diazotrophic unicellular cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(4):e1002460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002460. Epub 2012 Apr 5. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22529767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allahverdiyeva, Y., H. Leino, L. Saari, D. P. Fewer, S. Shunmugam, K. Sivonen, and E.-M. Aro. 2010. Screening for biohydrogen production by cyanobacteria isolated from the Baltic Sea and Finnish lakes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35:1117-1127.
-
- Berberoğlu, H., J. Jay, and L. Pilon. 2008. Effect of nutrient media on photobiological hydrogen production by Anabaena variabilis ATCC 29413. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 33:1172-1184.
-
- Bernát, G., N. Waschewski, and M. Rogner. 2009. Towards efficient hydrogen production: the impact of antenna size and external factors on electron transport dynamics in Synechocystis PCC 6803. Photosynth. Res. 99:205-216. - PubMed
-
- Burrows, E. H., F. W. R. Chaplen, and R. L. Ely. 2008. Optimization of media nutrient composition for increased photofermentative hydrogen production by Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 33:6092-6099.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

