Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing
- PMID: 20453866
- PMCID: PMC2879396
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1459
Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing
Abstract
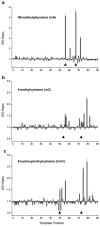
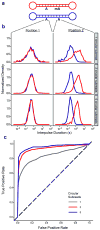
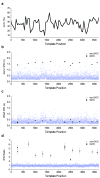
We describe the direct detection of DNA methylation, without bisulfite conversion, through single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing. In SMRT sequencing, DNA polymerases catalyze the incorporation of fluorescently labeled nucleotides into complementary nucleic acid strands. The arrival times and durations of the resulting fluorescence pulses yield information about polymerase kinetics and allow direct detection of modified nucleotides in the DNA template, including N6-methyladenine, 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Measurement of polymerase kinetics is an intrinsic part of SMRT sequencing and does not adversely affect determination of primary DNA sequence. The various modifications affect polymerase kinetics differently, allowing discrimination between them. We used these kinetic signatures to identify adenine methylation in genomic samples and found that, in combination with circular consensus sequencing, they can enable single-molecule identification of epigenetic modifications with base-pair resolution. This method is amenable to long read lengths and will likely enable mapping of methylation patterns in even highly repetitive genomic regions.
Figures
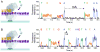

Comment in
-
Zeroing in on DNA methylomes with no BS.Nat Methods. 2010 Jun;7(6):435-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0610-435. Nat Methods. 2010. PMID: 20508637 No abstract available.
-
Technology: DNA methylation while you sequence.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Jul;11(7):454. doi: 10.1038/nrg2817. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 20517344 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gardiner-Garden M, Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987;196:261–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

