Effects of sildenafil on autonomic nervous function during sleep in obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 20454497
- PMCID: PMC2862674
- DOI: 10.1590/S1807-59322010000400008
Effects of sildenafil on autonomic nervous function during sleep in obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of sildenafil on the autonomic nervous system in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
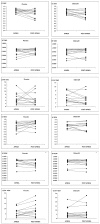
Methods: Thirteen male patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea (mean age 43+/-10 years with a mean body mass index of 26.7+/-1.9 kg/m(2)) received a single 50-mg dose of sildenafil or a placebo at bedtime. All-night polysomnography and heart rate variability were recorded. Frequency domain analysis of heart rate variability was performed for the central five-minute sample of the longest uninterrupted interval of slow wave and rapid eye movement sleep, as well as for one-minute samples during apnea and during slow wave and rapid eye movement sleep after resumption of respiration.
Results: Compared to the placebo, sildenafil was associated with an increase in the normalized high-frequency (HF(nu)) components and a decrease in the low/high-frequency components of the heart rate variability ratio (LF/HF) in slow wave sleep (p<0.01 for both). Differences in heart rate variability parameters between one-minute post-apnea and apnea samples (Delta = difference between resumption of respiration and apnea) were assessed. A trend toward a decreasing magnitude of DeltaLF activity was observed during rapid eye movement sleep with sildenafil in comparison to placebo (p=0.046). Additionally, DeltaLF/HF in SWS and rapid eye movement sleep was correlated with mean desaturation (s(R =) -0.72 and -0.51, respectively, p= 0.01 for both), and DeltaHF(nu) in rapid eye movement sleep was correlated with mean desaturation (s(R=) 0.66, p= 0.02) and the desaturation index (s(R=) 0.58, p = 0.047).
Conclusions: The decrease in arousal response to apnea/hypopnea events along with the increase in HF(nu) components and decrease in LH/HF components of the heart rate variability ratio during slow wave sleep suggest that, in addition to worsening sleep apnea, sildenafil has potentially immediate cardiac effects in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; Heart rate variability; Nitric oxide; Oxyhemoglobin; Phosphodiesterase-5.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of sildenafil on sleep respiratory parameters and heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Med. 2010 Jun;11(6):545-51. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2010.02.010. Epub 2010 May 15. Sleep Med. 2010. PMID: 20472498 Clinical Trial.
-
A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study of sildenafil in obstructive sleep apnea.Arch Intern Med. 2006 Sep 18;166(16):1763-7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.16.1763. Arch Intern Med. 2006. PMID: 16983056 Clinical Trial.
-
The association between obstructive sleep apnea during REM sleep and autonomic dysfunction as measured by heart rate variability.Sleep Breath. 2019 Sep;23(3):865-871. doi: 10.1007/s11325-018-01779-y. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Sleep Breath. 2019. PMID: 30685848
-
Safety of sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007 Jul;6(4):423-30. doi: 10.1517/14740338.6.4.423. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007. PMID: 17688386 Review.
-
Obstructive sleep apnea heterogeneity and autonomic function: a role for heart rate variability in therapy selection and efficacy monitoring.J Sleep Res. 2024 Feb;33(1):e14020. doi: 10.1111/jsr.14020. Epub 2023 Sep 14. J Sleep Res. 2024. PMID: 37709966 Review.
Cited by
-
A negative expiratory pressure test during wakefulness for evaluating the risk of obstructive sleep apnea in patients referred for sleep studies.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011;66(11):1887-94. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322011001100007. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011. PMID: 22086518 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of heart rate on reproducibility of heart rate variability analysis in the supine and standing positions in healthy men.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019;74:e806. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2019/e806. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31411277 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of obstructive sleep apnea and its treatment over the erectile function: a systematic review.Asian J Androl. 2017 May-Jun;19(3):303-310. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.170440. Asian J Androl. 2017. PMID: 26763546 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and hypercapnia inhibit hypothalamic orexin neurons in rats.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Nov 1;116(5):2250-2259. doi: 10.1152/jn.00196.2016. Epub 2016 Aug 24. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27559138 Free PMC article.
-
Tonsil volume, tonsil grade and obstructive sleep apnea: is there any meaningful correlation?Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011;66(8):1347-52. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000800007. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011. PMID: 21915482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep- disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–5. - PubMed
-
- Knorst MM, Souza FJ, Martinez D. Obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome: association with gender, obesity and sleepiness-related factors. J Bras Pneumol. 2008;34:490–6. - PubMed
-
- Lima AM, Franco CM, Castro CM, Bezerra Ade A, Ataíde L, Jr, Halpern A. Obstructive sleep apnea contribution to oxidative stress in obesity. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2008;52:668–76. - PubMed
-
- Fanfulla F, Malaguti S, Montagna T, Salvani S, Bruschi C, Crotti P, et al. Erectile dysfunction in men with obstructive sleep apnea: an early sign of nerve involvement. Sleep. 2000;23:775–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous