Combination of bifunctional alkylating agent and arsenic trioxide synergistically suppresses the growth of drug-resistant tumor cells
- PMID: 20454509
- PMCID: PMC2864475
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.10110
Combination of bifunctional alkylating agent and arsenic trioxide synergistically suppresses the growth of drug-resistant tumor cells
Abstract
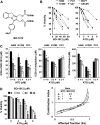
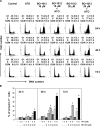
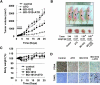
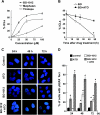
Drug resistance is a crucial factor in the failure of cancer chemotherapy. In this study, we explored the effect of combining alkylating agents and arsenic trioxide (ATO) on the suppression of tumor cells with inherited or acquired resistance to therapeutic agents. Our results showed that combining ATO and a synthetic derivative of 3a-aza-cyclopenta[a]indenes (BO-1012), a bifunctional alkylating agent causing DNA interstrand cross-links, was more effective in killing human cancer cell lines (H460, H1299, and PC3) than combining ATO and melphalan or thiotepa. We further demonstrated that the combination treatment of H460 cells with BO-1012 and ATO resulted in severe G(2)/M arrest and apoptosis. In a xenograft mouse model, the combination treatment with BO-1012 and ATO synergistically reduced tumor volumes in nude mice inoculated with H460 cells. Similarly, the combination of BO-1012 and ATO effectively reduced the growth of cisplatin-resistant NTUB1/P human bladder carcinoma cells. Furthermore, the repair of BO-1012-induced DNA interstrand cross-links was significantly inhibited by ATO, and consequently, gammaH2AX was remarkably increased and formed nuclear foci in H460 cells treated with this drug combination. In addition, Rad51 was activated by translocating and forming foci in nuclei on treatment with BO-1012, whereas its activation was significantly suppressed by ATO. We further revealed that ATO might mediate through the suppression of AKT activity to inactivate Rad51. Taken together, the present study reveals that a combination of bifunctional alkylating agents and ATO may be a rational strategy for treating cancers with inherited or acquired drug resistance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel combination therapy with arsenic trioxide and parthenolide against pancreatic cancer cells.Pancreas. 2009 May;38(4):e114-23. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181a0b6f2. Pancreas. 2009. PMID: 19342982
-
Combination of arsenic trioxide and chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2013 Nov;82(2):222-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.08.022. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24041618
-
Shikonin potentiates the effect of arsenic trioxide against human hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):70504-70515. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12041. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27655700 Free PMC article.
-
Biological responses to arsenic compounds.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 10;284(28):18583-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R900003200. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19363033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alkylating anticancer agents and their relations to microRNAs.Cancer Drug Resist. 2019 Mar 19;2(1):1-17. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.09. eCollection 2019. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 35582140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Celecoxib-induced cytotoxic effect is potentiated by inhibition of autophagy in human urothelial carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 9;8(12):e82034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082034. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349176 Free PMC article.
-
Increased growth-inhibitory and cytotoxic activity of arsenic trioxide in head and neck carcinoma cells with functional p53 deficiency and resistance to EGFR blockade.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 13;9(6):e98867. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098867. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24927258 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy Metal Exposure Influences Double Strand Break DNA Repair Outcomes.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 11;11(3):e0151367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151367. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26966913 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin promotes Temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma by orchestrating DNA repair and tumor stemness.Oncogene. 2015 Apr 2;34(14):1853-64. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.92. Epub 2014 May 5. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24793792
-
Comparison of optical and power Doppler ultrasound imaging for non-invasive evaluation of arsenic trioxide as a vascular disrupting agent in tumors.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46106. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046106. Epub 2012 Sep 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wadhwa PD, Zielske SP, Roth JC, Ballas CB, Bowman JE, Gerson SL. Cancer gene therapy: scientific basis. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:437–452. - PubMed
-
- Musto P, D'Auria F. Melphalan: old and new uses of a still master drug for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16:1467–1487. - PubMed
-
- La Rocca RV, Mehdorn HM. Localized BCNU chemotherapy and the multimodal management of malignant glioma. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25:149–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
