Interferon gamma-induced human guanylate binding protein 1 inhibits mammary tumor growth in mice
- PMID: 20454519
- PMCID: PMC2864808
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2009.00172
Interferon gamma-induced human guanylate binding protein 1 inhibits mammary tumor growth in mice
Abstract
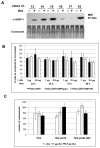
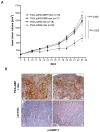
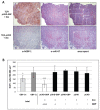
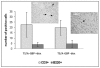
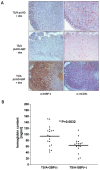
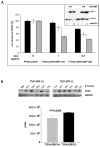
Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) has recently been implicated in cancer immunosurveillance. Among the most abundant proteins induced by IFN-gamma are guanylate binding proteins (GBPs), which belong to the superfamily of large GTPases and are widely expressed in various species. Here, we investigated whether the well-known human GBP-1 (hGBP-1), which has been shown to exert antiangiogenic activities and was described as a prognostic marker in colorectal carcinomas, may contribute to an IFN-gamma-mediated tumor defense. To this end, an IFN-independent, inducible hGBP-1 expression system was established in murine mammary carcinoma (TS/A) cells, which were then transplanted into syngeneic immune-competent Balb/c mice. Animals carrying TS/A cells that had been given doxycycline for induction of hGBP-1 expression revealed a significantly reduced tumor growth compared with mock-treated mice. Immunohistochemical analysis of the respective tumors demonstrated a tightly regulated, high-level expression of hGBP-1. No signs of an enhanced immunosurveillance were observed by investigating the number of infiltrating B and T cells. However, hemoglobin levels as well as the number of proliferating tumor cells were shown to be significantly reduced in hGBP-1-expressing tumors. This finding corresponded to reduced amounts of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) released by hGBP-1-expressing TS/A cells in vitro and reduced VEGF-A protein levels in the corresponding mammary tumors in vivo. The results suggest that hGBP-1 may contribute to IFN-gamma-mediated antitumorigenic activities by inhibiting paracrine effects of tumor cells on angiogenesis. Consequently, owing to these activities GBPs might be considered as potent members in an innate, IFN-gamma-induced antitumoral defense system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-21 induces tumor rejection by specific CTL and IFN-gamma-dependent CXC chemokines in syngeneic mice.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1540-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1540. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734732
-
Golgi targeting of human guanylate-binding protein-1 requires nucleotide binding, isoprenylation, and an IFN-gamma-inducible cofactor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 14;102(24):8680-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503227102. Epub 2005 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15937107 Free PMC article.
-
Transfection of the genes for interleukin-12 into the K1735 melanoma and the EMT6 mammary sarcoma murine cell lines reveals distinct mechanisms of antitumor activity.Int J Cancer. 2003 Sep 20;106(5):690-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11284. Int J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12866028
-
Human guanylate binding protein-1 (hGBP-1) characterizes and establishes a non-angiogenic endothelial cell activation phenotype in inflammatory diseases.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2005;45:215-27. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2005.02.011. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2005. PMID: 16005050 Review.
-
Pathophysiological role of guanylate-binding proteins in gastrointestinal diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 28;22(28):6434-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6434. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27605879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IFN-γ and TNF-α-induced GBP-1 inhibits epithelial cell proliferation through suppression of β-catenin/TCF signaling.Mucosal Immunol. 2012 Nov;5(6):681-90. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.41. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Mucosal Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22692453 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic and Immunological Value of Guanylate-Binding Proteins in Lower-Grade Glioma: Potential Markers or Not?Front Genet. 2021 Oct 25;12:651348. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.651348. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34759950 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma interferon-induced guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel actin cytoskeleton remodeling factor.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;34(2):196-209. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00664-13. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24190970 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprofiling TS/A Murine Mammary Cancer for a Functional Precision Experimental Model.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 27;11(12):1889. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121889. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31783695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine-Induced Guanylate Binding Protein 1 (GBP1) Release from Human Ovarian Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 19;12(2):488. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020488. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32093058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:836–48. - PubMed
-
- Dighe AS, Richards E, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. Enhanced in vivo growth and resistance to rejection of tumor cells expressing dominant negative IFN gamma receptors. Immunity. 1994;1:447–56. - PubMed
-
- Kundu N, Beaty TL, Jackson MJ, Fulton AM. Antimetastatic and antitumor activities of interleukin 10 in a murine model of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:536–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

