How deeply cells feel: methods for thin gels
- PMID: 20454525
- PMCID: PMC2864502
- DOI: 10.1088/0953-8984/22/19/194116
How deeply cells feel: methods for thin gels
Abstract
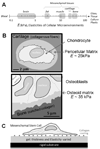
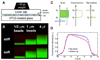
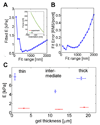
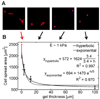
Tissue cells lack the ability to see or hear but have evolved mechanisms to feel into their surroundings and sense a collective stiffness. A cell can even sense the effective stiffness of rigid objects that are not in direct cellular contact - like the proverbial princess who feels a pea placed beneath soft mattresses. How deeply a cell feels into a matrix can be measured by assessing cell responses on a controlled series of thin and elastic gels that are affixed to a rigid substrate. Gel elasticity E is readily varied with polymer concentrations of now-standard polyacrylamide hydrogels, but to eliminate wrinkling and detachment of thin gels from an underlying glass coverslip, vinyl groups are bonded to the glass before polymerization. Gel thickness is nominally specified using micron-scale beads that act as spacers, but gels swell after polymerization as measured by z-section, confocal microscopy of fluorescent gels. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is used to measure E at gel surfaces, employing stresses and strains that are typically generated by cells and yielding values for E that span a broad range of tissue microenvironments. To illustrate cell sensitivities to a series of thin-to-thick gels, the adhesive spreading of mesenchymal stem cells was measured on gel mimics of a very soft tissue (eg. brain, E ~ 1 kPa). Initial results show that cells increasingly respond to the rigidity of an underlying 'hidden' surface starting at about 10-20 microm gel thickness with a characteristic tactile length of less than about 5 microm.
Figures


References
-
- Patel PN, Smith CK, Patrick CW. Rheological and recovery properties of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels and human adipose tissue. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. 2005 Jun 1;73A(3):313–319. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta M, Paolucci E, Stornaiuolo A, Cossu G, et al. Muscle regeneration by bone marrow derived myogenic progenitors. Science. 1998 Mar 6;279(5356):1528–1530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
