Physiological and histopathological investigations on the effects of alpha-lipoic acid in rats exposed to malathion
- PMID: 20454535
- PMCID: PMC2864892
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/203503
Physiological and histopathological investigations on the effects of alpha-lipoic acid in rats exposed to malathion
Abstract
The present study was designed to evaluate the influence of alpha-lipoic acid treatment in rats exposed to malathion. Forty adult male rats were used in this study and distributed into four groups. Animals of group 1 were untreated and served as control. Rats of group 2 were orally given malathion at a dose level of 100 mg/kg body weight (BW) for a period of one month. Experimental animals of group 3 were orally given alpha-lipoic acid at a dose level of 20 mg/kg BW and after 3 hours exposed to malathion at the same dose given to group 2. Rats of group 4 were supplemented with alpha-lipoic acid at the same dose given to group 3. The activities of serum glutamic oxaloacetic acid transaminase (GOT), glutamic pyruvic acid transaminase (GPT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and acid phosphatase (ACP), and the values of creatinine, urea, and uric acid were statistically increased, while the values of total protein and total albumin were significantly decreased in rats exposed to malathion. Moreover, administration of malathion for one month resulted in damage of liver and kidney structures. Administration of alpha-lipoic acid before malathion exposure to rat can prevent severe alterations of hemato-biochemical parameters and disruptions of liver and kidney structures. In conclusion, this study obviously demonstrated that pretreatment with alpha-lipoic acid significantly attenuated the physiological and histopathological alterations induced by malathion. Also, the present study identifies new areas of research for development of better therapeutic agents for liver, kidney, and other organs' dysfunctions and diseases.
Figures

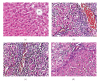
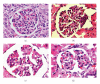
References
-
- Chaudhuri K, Selvaraj S, Pal AK. Studies on the genotoxicity of endosulfan in bacterial systems. Mutation Research. 1999;439(1):63–67. - PubMed
-
- Davis JE. Neurotoxic concerns of human pesticide exposures. American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 1991;18(3):327–331. - PubMed
-
- Mason HJ. The recovery of plasma cholinesterase and erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase activity in workers after over-exposure to dichlorvos. Occupational Medicine. 2000;50(5):343–347. - PubMed
-
- Nigg HN, Knaak JB. Blood cholinesterases as human biomarkers of organophosphorus pesticide exposure. Reviews of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology. 2000;163:29–111. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

