Platelet factor 4 regulation of monocyte KLF4 in experimental cerebral malaria
- PMID: 20454664
- PMCID: PMC2862712
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010413
Platelet factor 4 regulation of monocyte KLF4 in experimental cerebral malaria
Abstract
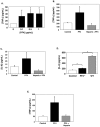
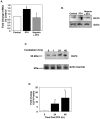
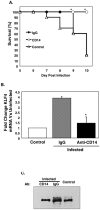
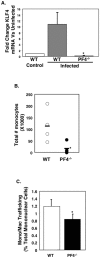
Cerebral malaria continues to be a difficult to treat complication of Plasmodium falciparum infection in children. We have shown that platelets can have major deleterious immune functions in experimental cerebral malaria (ECM). One of the platelet derived mediators we have identified as particularly important is platelet factor 4/CXCL4. Our prior work demonstrated that PF4(-/-) mice are protected from ECM, have reduced plasma cytokines, and have reduced T-cell trafficking to the brain. We now show that PF4 drives monocyte cytokine production in a Kruppel like factor 4 (KLF4) dependent manner. Monocyte depleted Plasmodium berghei infected mice have improved survival, and KLF4 is greatly increased in control, but not monocyte depleted mice. PF4(-/-) mice have less cerebral monocyte trafficking and no change in KLF4 expression. These data indicate that PF4 induction of monocyte KLF4 expression may be an important step in the pathogenesis of ECM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- van der Heyde HC, Nolan J, Combes V, Gramaglia I, Grau GE. A unified hypothesis for the genesis of cerebral malaria: sequestration, inflammation and hemostasis leading to microcirculatory dysfunction. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:503–508. - PubMed
-
- Smyth SS, McEver RP, Weyrich AS, Morrell CN, Hoffman MR, et al. Platelet functions beyond haemostasis. J Thromb Haemost 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

