Sensitivity of noninvasive prenatal detection of fetal aneuploidy from maternal plasma using shotgun sequencing is limited only by counting statistics
- PMID: 20454671
- PMCID: PMC2862719
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010439
Sensitivity of noninvasive prenatal detection of fetal aneuploidy from maternal plasma using shotgun sequencing is limited only by counting statistics
Abstract
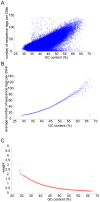
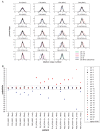
We recently demonstrated noninvasive detection of fetal aneuploidy by shotgun sequencing cell-free DNA in maternal plasma using next-generation high throughput sequencer. However, GC bias introduced by the sequencer placed a practical limit on the sensitivity of aneuploidy detection. In this study, we describe a method to computationally remove GC bias in short read sequencing data by applying weight to each sequenced read based on local genomic GC content. We show that sensitivity is limited only by counting statistics and that sensitivity can be increased to arbitrary precision in sample containing arbitrarily small fraction of fetal DNA simply by sequencing more DNA molecules. High throughput shotgun sequencing of maternal plasma DNA should therefore enable noninvasive diagnosis of any type of fetal aneuploidy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 88, December 2007. Invasive prenatal testing for aneuploidy. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110:1459–1467. - PubMed
-
- Dennis Lo YM, Chiu RW. Prenatal diagnosis: progress through plasma nucleic acids. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Chiu RW, Sun H, Akolekar R, Clouser C, Lee C, et al. Maternal Plasma DNA Analysis with Massively Parallel Sequencing by Ligation for Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Trisomy 21. Clin Chem 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

