Spatial distribution of factor Xa, thrombin, and fibrin(ogen) on thrombi at venous shear
- PMID: 20454680
- PMCID: PMC2861630
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010415
Spatial distribution of factor Xa, thrombin, and fibrin(ogen) on thrombi at venous shear
Abstract
Background: The generation of thrombin is a critical process in the formation of venous thrombi. In isolated plasma under static conditions, phosphatidylserine (PS)-exposing platelets support coagulation factor activation and thrombin generation; however, their role in supporting coagulation factor binding under shear conditions remains unclear. We sought to determine where activated factor X (FXa), (pro)thrombin, and fibrin(ogen) are localized in thrombi formed under venous shear.
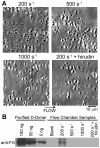
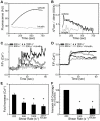
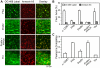
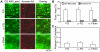
Methodology/principal findings: Fluorescence microscopy was used to study the accumulation of platelets, FXa, (pro)thrombin, and fibrin(ogen) in thrombi formed in vitro and in vivo. Co-perfusion of human blood with tissue factor resulted in formation of visible fibrin at low, but not at high shear rate. At low shear, platelets demonstrated increased Ca(2+) signaling and PS exposure, and supported binding of FXa and prothrombin. However, once cleaved, (pro)thrombin was observed on fibrin fibers, covering the whole thrombus. In vivo, wild-type mice were injected with fluorescently labeled coagulation factors and venous thrombus formation was monitored in mesenteric veins treated with FeCl(3). Thrombi formed in vivo consisted of platelet aggregates, focal spots of platelets binding FXa, and large areas binding (pro)thrombin and fibrin(ogen).
Conclusions/significance: FXa bound in a punctate manner to thrombi under shear, while thrombin and fibrin(ogen) distributed ubiquitously over platelet-fibrin thrombi. During thrombus formation under venous shear, thrombin may relocate from focal sites of formation (on FXa-binding platelets) to dispersed sites of action (on fibrin fibers).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thrombus growth and embolism on tissue factor-bearing collagen surfaces under flow: role of thrombin with and without fibrin.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Jun;32(6):1466-76. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.249789. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22516070 Free PMC article.
-
Factor VIII contributes to platelet-fibrin thrombus formation via thrombin generation under low shear conditions.Thromb Res. 2009 Nov;124(5):601-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2009.06.035. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Thromb Res. 2009. PMID: 19660789
-
Impaired thrombin generation in Reelin-deficient mice: a potential role of plasma Reelin in hemostasis.J Thromb Haemost. 2014 Dec;12(12):2054-64. doi: 10.1111/jth.12736. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25255925
-
Fibrinogen and red blood cells in venous thrombosis.Thromb Res. 2014 May;133 Suppl 1(0 1):S38-40. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.03.017. Thromb Res. 2014. PMID: 24759140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hysteresis-like binding of coagulation factors X/Xa to procoagulant activated platelets and phospholipids results from multistep association and membrane-dependent multimerization.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jun;1858(6):1216-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26874201 Review.
Cited by
-
Rate-limiting roles of the tenase complex of factors VIII and IX in platelet procoagulant activity and formation of platelet-fibrin thrombi under flow.Haematologica. 2015 Jun;100(6):748-56. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.116863. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25769543 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet Membrane Receptor Proteolysis: Implications for Platelet Function.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jan 8;7:608391. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.608391. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33490118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombus growth and embolism on tissue factor-bearing collagen surfaces under flow: role of thrombin with and without fibrin.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Jun;32(6):1466-76. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.249789. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22516070 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of volume, mass, and density of thrombus formation using brightfield and differential interference contrast microscopy.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Jan;18(1):16014. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.1.016014. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23348747 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous modification of platelet membranes with the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA reduces platelet procoagulant activity and thrombus formation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Feb 1;304(3):C273-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00174.2012. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23174566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nesbitt WS, Westein E, Tovar-Lopez FJ, Tolouei E, Mitchell A, et al. A shear gradient-dependent platelet aggregation mechanism drives thrombus formation. Nat Med. 2009;15:665–673. - PubMed
-
- Kuijpers MJ, Munnix IC, Cosemans JM, Vlijmen BV, Reutelingsperger CP, et al. Key role of platelet procoagulant activity in tissue factor-and collagen-dependent thrombus formation in arterioles and venules in vivo differential sensitivity to thrombin inhibition. Microcirculation. 2008;15:269–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

