Manganese displacement from Zinpyr-1 allows zinc detection by fluorescence microscopy and magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 20454746
- PMCID: PMC2880654
- DOI: 10.1039/c0cc00179a
Manganese displacement from Zinpyr-1 allows zinc detection by fluorescence microscopy and magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
A paramagnetic manganese complex of a fluorescein-based probe affords a dual-modality zinc sensor featuring an improved fluorescence dynamic range and an MRI readout.
Figures
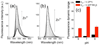



Similar articles
-
Understanding zinc quantification with existing and advanced ditopic fluorescent Zinpyr sensors.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Mar 23;133(11):4101-14. doi: 10.1021/ja110907m. Epub 2011 Feb 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21351756 Free PMC article.
-
A dual-responsive probe for detecting cellular hypoxia using 19F magnetic resonance and fluorescence.Chem Commun (Camb). 2019 Jul 23;55(60):8860-8863. doi: 10.1039/c9cc00375d. Chem Commun (Camb). 2019. PMID: 31219109 Free PMC article.
-
New strategy for quantifying biological zinc by a modified zinpyr fluorescence sensor.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Nov 26;130(47):15788-9. doi: 10.1021/ja807156b. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18975868 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging mobile zinc in biology.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010 Apr;14(2):225-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.12.010. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 20097117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ratio imaging: practical considerations for measuring intracellular calcium and pH in living tissue.Methods Cell Biol. 1998;56:237-51. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60429-x. Methods Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9500141 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mobile zinc as a modulator of sensory perception.FEBS Lett. 2023 Jan;597(1):151-165. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14544. Epub 2022 Dec 20. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36416529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal Sequestration and Antimicrobial Activity of Human Calprotectin Are pH-Dependent.Biochemistry. 2020 Jul 7;59(26):2468-2478. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00359. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32491853 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese and microbial pathogenesis: sequestration by the Mammalian immune system and utilization by microorganisms.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):641-51. doi: 10.1021/cb500792b. Epub 2015 Jan 16. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25594606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Gd(III)-Based Contrast Agents: Challenges and Key Advances.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Oct 30;141(43):17025-17041. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b09149. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31593630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel zinc bis(thiosemicarbazone) complex for live cell imaging.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011 Apr;16(4):621-32. doi: 10.1007/s00775-011-0764-0. Epub 2011 Mar 8. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21384247
References
-
- Nguyen BT, Anslyn EV. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006;250:3118–3127.
-
- Fabbrizzi L, Leone A, Taglietti A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001;40:3066–3069. - PubMed
-
- Tobey SL, Anslyn EV. Org. Lett. 2003;5:2029–2031. - PubMed
-
- Hilderbrand SA, Lim MH, Lippard SJ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:4972–4978. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Baek K-H, Kim HN, Cui J, Qian X, Spring DR, Shin I, Yoon J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:601–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

