Behavioral assessment and management of food refusal in children with cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 2045484
- PMCID: PMC10276582
Behavioral assessment and management of food refusal in children with cystic fibrosis
Abstract
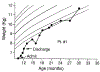
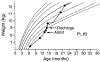
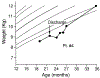
Four children with cystic fibrosis, ranging in age from 10 to 40 months, were admitted to a specialized pediatric unit for evaluation and treatment of malnutrition. All were below the fifth percentile for weight despite appropriate pancreatic enzyme replacement and outpatient nutritional counseling. Dietary evaluation revealed oral intake of 48% to 62% of that required for growth. Standardized nursing and psychological assessments of feeding behaviors during meals indicated a low acceptance rate of foods and a high rate of maladaptive feeding behaviors. Treatment consisted of behavioral management using positive reinforcement of food acceptance, extinction of negative behaviors, and parent training. Mean percentage of caloric intake increased from 54% to 92% for the four patients. At long-term follow-up, the patients who continued the program demonstrated substantial and persistent catch-up growth. Behavioral feeding disorders may contribute to failure to thrive in patients with cystic fibrosis and must be considered when growth failure occurs despite correct medical management and apparently mild pulmonary and gastrointestinal involvement.
Figures
References
-
- Matthews L, Drotar D: Cystic fibrosis: A challenging long-term chronic disease. Pediatr Clin North Am 1:133–52, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Bell L, Durie P. Forstner G: What do children with cystic fibrosis eat? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 3:137–146, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Smith AE, Lloyd-Still JD: Value of computerized dietary analysis in pediatric nutrition: An analysis of 147 patients. J Pediatr 103:820–823, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Hubbard VS: Nutritional considerations in CF. Semin Resp Med 6:308–313, 1985
-
- Fischer-Fay A, Goldberg S, Simmons RJ, et al. Chronic illness and infant-mother attachment. J Dev Behav Pediatr 9:266–270, 1988 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical