Effect of α-tocopherol supplementation on in vitro maturation of sheep oocytes and in vitro development of preimplantation sheep embryos to the blastocyst stage
- PMID: 20454845
- PMCID: PMC2941590
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-010-9430-7
Effect of α-tocopherol supplementation on in vitro maturation of sheep oocytes and in vitro development of preimplantation sheep embryos to the blastocyst stage
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the effects of α-tocopherol supplementation to oocyte maturation media and embryo culture media on the yield of ovine embryos.
Methods: α-tocopherol, at concentrations of 0, 50, 100, 200, 400 and 500 µM was supplemented to ovine oocyte or embryo culture media and cultured at 5% or 20% O(2) levels. Percentages of cleavage, morula and blastocyst, total cell count and comet assay were taken as indicators of developmental competence of embryos.
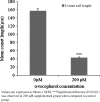
Results: 200 µM α-tocopherol in embryo culture medium at 20% O(2) level significantly increased the rates of cleavage (P < 0.05), morulae (P < 0.05) and blastocyst (P < 0.01) formation and blastocyst total cell number (P < 0.01) when compared with control. The rates of blastocyst formation were also significantly higher in 100 µM (P < 0.01) and 400 µM (P < 0.05) supplemented groups than control.
Conclusion: α-tocopherol supplementation may enhance the in vitro developmental competence of ovine embryos by protecting them from oxidative damage.
Figures
References
-
- Camargo LSA, Viana JHM, Sa WF, Ferreira AM, Ramos AA, Filho VRV. Factors influencing in vitro embryo production. Anim Reprod. 2006;3(1):19–28.
-
- Nasr-Esfahani MM, Johnson MH. The origin of reactive oxygen species in mouse embryos cultured in vitro. Development. 1991;113(2):551–560. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical