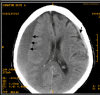
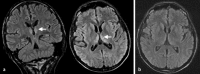
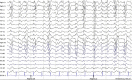
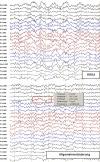
[Diagnostic work-up and treatment of acute psycho-organic syndrome]
- PMID: 20454878
- PMCID: PMC7095979
- DOI: 10.1007/s00115-010-3013-9
[Diagnostic work-up and treatment of acute psycho-organic syndrome]
Abstract
Psychiatric disorders due to a medical or neurological condition are the main differential diagnoses in newly admitted psychiatric patients, consultations and outpatient settings. Especially with the growing elderly population delirium occurs more frequently, often due to multiple causes. Although its prognosis is known to be unfavourable, delirium too often remains undiagnosed or untreated. Medications, neurological diseases, infections as well as metabolic and other medical conditions have to be ruled out in the differential diagnosis using the patient's history, physical examination, laboratory results and imaging procedures. First-time psychiatric symptoms of an unknown medical disease as well as co-occurring psychiatric symptoms in chronic diseases provoke a challenging diagnostic decision, as reactive psychiatric symptoms have to be distinguished which is not always possible. In psychiatric disorders confirmed to be due to a medical condition, therapeutic implications are primarily geared to the causes of the disease. Only in a second step psychiatric medication is warranted with antipsychotic, antidepressant or sedation-inducing properties depending on the patient's symptoms.
Organische Ursachen akuter psychiatrischer Syndrome stellen die wichtigste Differenzialdiagnose bei psychiatrischen Akutaufnahmen, im Konsiliardienst und ambulanten Notdienst dar. Gerade mit der wachsenden Gruppe älterer Patienten treten Delirien, oft multifaktoriell ausgelöst, sehr häufig auf. Trotz ihrer ungünstigen Prognose bleiben sie allerdings zu oft unerkannt und unbehandelt. Medikamentöse, akutneurologische, infektiöse, metabolische und andere somatische Ursachen müssen differenzialdiagnostisch fundiert durch Anamnese, körperlichen Befund, Labor und Bildgebung ausgeschlossen werden. Erstmanifestationen wie auch psychiatrische Begleitsymptome stellen oft eine differenzialdiagnostische Herausforderung dar, auch in der teilweise allerdings nicht sicher möglichen Abgrenzung von reaktiven psychischen Störungen.
Bestätigt sich eine organische Ursache, ist die Therapie primär ursachenorientiert und erst in einem zweiten Schritt symptomatisch mit antipsychotischer, antidepressiver oder sedierender Medikation. Einer iatrogenen Verursachung von Delirien sowie deren Prävention gilt ein besonderes Augenmerk, um die medizinische Qualität gerade für Ältere zu verbessern.
Similar articles
-
Psychogenic amnesia.Am Fam Physician. 1990 Jan;41(1):229-34. Am Fam Physician. 1990. PMID: 2403726 Review.
-
[Dysphagia or dysphagias during neuroleptic medication?].Encephale. 2012 Sep;38(4):351-5. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 22980477 French.
-
[Deaths in a Tunisian psychiatric hospital: an eleven-year retrospective study].Encephale. 2014 Oct;40(5):416-22. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2014.07.007. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Encephale. 2014. PMID: 25132014 French.
-
Symptoms of epilepsy and organic brain dysfunctions in patients with acute, brief depression combined with other fluctuating psychiatric symptoms: a controlled study from an acute psychiatric department.BMC Psychiatry. 2009 Sep 30;9:63. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-9-63. BMC Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19793395 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) acute day hospital versus admission; (2) vocational rehabilitation; (3) day hospital versus outpatient care.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(21):1-75. doi: 10.3310/hta5210. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532238 Review.
Cited by
-
[Psychiatric and psychosomatic consulation-liaison. An overview].Nervenarzt. 2013 May;84(5):639-47; quiz 648-9. doi: 10.1007/s00115-013-3771-2. Nervenarzt. 2013. PMID: 23595917 Review. German.
-
[Nonpharmaceutical concepts for prevention and treatment of delirium].Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2021 Dec;54(8):759-767. doi: 10.1007/s00391-021-01988-3. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2021. PMID: 34817684 Review. German.
-
[HELP - Hospital Elder Life Program - multimodal delirium prevention in elderly patients].Internist (Berl). 2017 Feb;58(2):125-131. doi: 10.1007/s00108-016-0181-0. Internist (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28120023 Review. German.
-
[Treatment with psychotropic agents in patients with dementia and delirium : Gap between guideline recommendations and treatment practice].Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2017 Feb;50(2):106-114. doi: 10.1007/s00391-016-1176-0. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2017. PMID: 28124100 Review. German.
References
-
- Arolt Dtsch Ärztebl. 1997;94:1354.
-
- Arolt Nervenarzt. 1995;66:347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical