Diffusion as a probe of the heterogeneity of antimicrobial peptide-membrane interactions
- PMID: 20455545
- PMCID: PMC2881297
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100426p
Diffusion as a probe of the heterogeneity of antimicrobial peptide-membrane interactions
Abstract
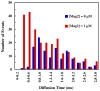
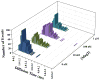
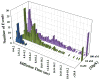
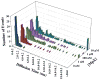
Many antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) function by forming various oligomeric structures and/or pores upon binding to bacterial membranes. Because such peptide aggregates are capable of inducing membrane thinning and membrane permeabilization, we expected that AMP binding would also affect the diffusivity or mobility of the lipid molecules in the membrane. Herein, we show that measurements of the diffusion times of individual lipids through a confocal volume via fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) provide a sensitive means of probing the underlying AMP-membrane interactions. In particular, results obtained with two well-studied AMPs, magainin 2 and mastoparan X, and two model membranes indicate that this method is capable of revealing structural information, especially the heterogeneity of the peptide-membrane system, that is otherwise difficult to obtain using common ensemble methods. Moreover, because of the high sensitivity of FCS, this method allows examination of the effect of AMPs on the membrane structure at very low peptide/lipid ratios.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial peptide interactions with bacterial cell membranes.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025 Jun;43(9):4615-4628. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2024.2304683. Epub 2024 Jan 23. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025. PMID: 38263741
-
Magainin 2 revisited: a test of the quantitative model for the all-or-none permeabilization of phospholipid vesicles.Biophys J. 2009 Jan;96(1):116-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.09.017. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19134472 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced membrane pore formation by multimeric/oligomeric antimicrobial peptides.Biochemistry. 2007 Nov 20;46(46):13437-42. doi: 10.1021/bi7015553. Epub 2007 Oct 18. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17944489
-
Magainins as paradigm for the mode of action of pore forming polypeptides.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Nov 10;1376(3):391-400. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4157(98)00014-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9804997 Review.
-
Elementary Processes and Mechanisms of Interactions of Antimicrobial Peptides with Membranes-Single Giant Unilamellar Vesicle Studies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1117:17-32. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-3588-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30980351 Review.
Cited by
-
Diffusion as a probe of peptide-induced membrane domain formation.Biochemistry. 2011 Mar 29;50(12):2291-7. doi: 10.1021/bi102068j. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21332237 Free PMC article.
-
Leaflet by Leaflet Synergistic Effects of Antimicrobial Peptides on Bacterial and Mammalian Membrane Models.J Phys Chem Lett. 2023 Apr 27;14(16):3920-3928. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c00119. Epub 2023 Apr 19. J Phys Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37075204 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic studies of protein folding: linear and nonlinear methods.Protein Sci. 2012 Feb;21(2):157-70. doi: 10.1002/pro.2006. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22109973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy measurements of the membrane protein TetA in Escherichia coli suggest rapid diffusion at short length scales.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048600. Epub 2012 Oct 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23119068 Free PMC article.
-
Divalent cation-induced cluster formation by polyphosphoinositides in model membranes.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Feb 22;134(7):3387-95. doi: 10.1021/ja208640t. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22280226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dathe M, Wieprecht T. Structural features of helical antimicrobial peptides: their potential to modulate activity on model membranes and biological cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1462:71–87. - PubMed
-
- Sato H, Feix JB. Peptide-membrane interactions and mechanisms of membrane destruction by amphipathic alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:1245–1256. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzaki K, Murase O, Miyahjima K. Kinetics of pore formation by an antimicrobial peptide, magainin 2, in phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1995;34:12553–12559. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzaki K, Yoneyama S, Murase O, Miyahima K. Transbilayer transport of ions and lipids coupled with mastoparan X translocation. Biochemistry. 1996;35:8450–8456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

