Dopamine D1 and D3 receptors are differentially involved in cue-elicited cocaine seeking
- PMID: 20456009
- PMCID: PMC2910121
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06775.x
Dopamine D1 and D3 receptors are differentially involved in cue-elicited cocaine seeking
Abstract
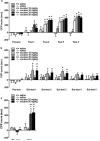
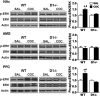
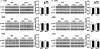
Environmental cues previously associated with reinforcing drugs can play a key role in relapse to drug seeking behaviors in humans. The mesocorticolimbic dopamine system plays a critical role in cocaine-induced neurobiological changes. Dopamine D1 and D3 receptors modulate locomotor-stimulant and positive reinforcing effects of cocaine, and cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking. Moreover, activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) induced by acute cocaine administration is regulated by both D1 and D3 receptors. How D1 and D3 receptors modulate the acquisition and extinction of cue-elicited cocaine seeking behavior and associated changes in the MAPK signaling pathway in different brain regions, however, remains unclear. In the present study, we found that D1 receptor mutant mice failed to acquire conditioned place preference (CPP) while D3 receptor mutant mice show delayed CPP extinction compared with wild-type mice. Moreover, ERK, but not the c-jun N-terminal kinase and p38, is activated in wild-type and D3 receptor mutant mice but not in D1 receptor mutant mice following CPP acquisition. D3 receptor mutant mice also exhibit sustained ERK activation compared with wild-type mice following extinction training. Our results suggest that D1 and D3 receptors differentially contribute to learned association between cues and the rewarding properties of cocaine by regulating, at least in part, ERK activation in specific areas of the brain.
Figures
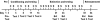





Similar articles
-
Activation of dopamine D3 receptors inhibits reward-related learning induced by cocaine.Neuroscience. 2011 Mar 10;176:152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.12.008. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21168475 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite regulation of cocaine-induced intracellular signaling and gene expression by dopamine D1 and D3 receptors.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Aug;1074:1-12. doi: 10.1196/annals.1369.001. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17105899
-
Dopamine D(1) and D(3) receptors oppositely regulate NMDA- and cocaine-induced MAPK signaling via NMDA receptor phosphorylation.J Neurochem. 2007 Oct;103(2):840-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04840.x. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17897358
-
Dopamine D1 and D3 receptor polypharmacology as a potential treatment approach for substance use disorder.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Jun;89:13-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 29577963 Review.
-
Is p38 MAPK Associated to Drugs of Abuse-Induced Abnormal Behaviors?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 8;21(14):4833. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144833. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32650599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture reduces cocaine-induced seizures and mortality in mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:134610. doi: 10.1155/2013/134610. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23690833 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D3 receptors regulate reconsolidation of cocaine memory.Neuroscience. 2013 Jun 25;241:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23506736 Free PMC article.
-
Amphetamine increases phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK at synaptic sites in the rat striatum and medial prefrontal cortex.Brain Res. 2013 Feb 4;1494:101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.11.038. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23201445 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine induces alterations in the long non-coding RNAs expression profile in the nucleus accumbens of the mouse.BMC Neurosci. 2015 Mar 25;16:18. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0157-3. BMC Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25884509 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, pharmacological evaluation and molecular modeling studies of triazole containing dopamine D3 receptor ligands.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Feb 1;25(3):519-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.12.023. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25556097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JP, Sweatt JD. Molecular psychology: Roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002;42:135–163. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharm. 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Berglind WJ, Case JM, Parker MP, Fuchs RA, See RE. Dopamine D1 or D2 receptor antagonism within the basolateral amygdala differentially alters the acquisition of cocaine-cue associations necessary for cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking. Neurosci. 2006;137:699–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

