Practical steps to improving the management of type 1 diabetes: recommendations from the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management
- PMID: 20456170
- PMCID: PMC2814087
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02296.x
Practical steps to improving the management of type 1 diabetes: recommendations from the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management
Abstract
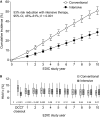
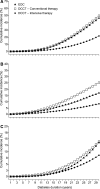
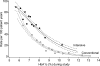
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) led to considerable improvements in the management of type 1 diabetes, with the wider adoption of intensive insulin therapy to reduce the risk of complications. However, a large gap between evidence and practice remains, as recently shown by the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications (EDC) study, in which 30-year rates of microvascular complications in the 'real world' EDC patients were twice that of DCCT patients who received intensive insulin therapy. This gap may be attributed to the many challenges that patients and practitioners face in the day-to-day management of the disease. These barriers include reaching glycaemic goals, overcoming the reality and fear of hypoglycaemia, and appropriate insulin therapy and dose adjustment. As practitioners, the question remains: how do we help patients with type 1 diabetes manage glycaemia while overcoming barriers? In this article, the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management provides practical recommendations to help improve the care of patients with type 1 diabetes.
Figures
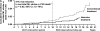
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . Diabetes Atlas. Brussels, Belgium: IDF; 2007.
-
- DCCT/EDIC Research Group Modern-day clinical course of type 1 diabetes mellitus after 30 years’ duration: the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications and Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications experience (1983-2005) Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:1307–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Concannon P, Rich SS, Nepom GT. Genetics of type 1A diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1646–54. - PubMed
-
- Bruno G, Cerutti F, Merletti F, et al. Residual beta-cell function and male/female ratio are higher in incident young adults than in children: the registry of type 1 diabetes of the province of Turin, Italy, 1984-2000. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:312–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

