Topical levofloxacin 1.5% overcomes in vitro resistance in rabbit keratitis models
- PMID: 20456251
- PMCID: PMC4739651
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2010.01897.x
Topical levofloxacin 1.5% overcomes in vitro resistance in rabbit keratitis models
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether topical levofloxacin 1.5% will successfully treat both levofloxacin-resistant and susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (SA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) in rabbit keratitis models.
Methods: For levofloxacin-resistant and susceptible SA, respectively, 32 New Zealand White (NZW) rabbits were intrastromally injected with 1000 colony-forming units (CFU). After 4 hr, the corneas of eight rabbits were homogenized to determine onset CFU/ml. Twenty-four rabbits were divided into three treatments: levofloxacin, vancomycin (cefazolin for levofloxacin-susceptible SA) and saline. Twenty-one drops were administered over 5 hr. One hour post-treatment, the corneas were homogenized for CFU/ml. For levofloxacin-resistant and susceptible PA, respectively, 32 NZW rabbits were intrastromally injected with 1000 CFU. After 16 hr, the corneas of eight rabbits were homogenized for CFU/ml. Twenty-four rabbits were divided into three treatments: levofloxacin, tobramycin (ciprofloxacin for levofloxacin-susceptible PA) and saline. Nineteen drops were administered over 8 hr. One hour post-treatment, the corneas were homogenized for CFU/ml. The CFU/ml data were analysed for sterilization and non-parametrically for reduction.
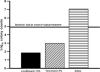
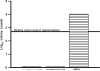
Results: Levofloxacin 1.5% significantly reduced more (p < 0.05) levofloxacin-resistant SA than vancomycin; was equivalent to cefazolin (p > 0.05) for levofloxacin-susceptible SA; was equivalent to tobramycin for levofloxacin-resistant PA; was equivalent to ciprofloxacin for levofloxacin-susceptible PA; and significantly reduced more SA and PA than saline and onset. Levofloxacin 1.5% sterilized the corneas in the levofloxacin-resistant and susceptible PA groups (32/32) and levofloxacin-susceptible SA group (16/16), but not the levofloxacin-resistant SA group (0/16).
Conclusion: Levofloxacin 1.5% was effective for reducing SA and PA in the rabbit keratitis models regardless of in vitro resistance.
Figures


References
-
- Callegan MC, Engel LS, Hill JM, O'Callaghan RJ. Ciprofloxacin versus tobramycin for the treatment of Staphylococcus keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:1033–1037. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Methods for Dilution Antimicrobials Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 7 edn. Approved standard. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne, PA: 2006. document M7-A6, vol.23, No.2.
-
- Dajcs JJ, Moreau JM, Stroman DW, et al. The effectiveness of tobramycin and ocuflox in a prophylaxis model of Staphylococcus keratitis. Curr Eye Res. 2001;23:60–63. - PubMed
-
- Kowalski RP, Romanowski EG, Yates KA, Gordon YJ. Lomefloxacin is an effective treatment for experimental bacterial keratitis. Cornea. 2001;20:306–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

