Protective effect of eotaxin-2 inhibition in adjuvant-induced arthritis
- PMID: 20456418
- PMCID: PMC2909409
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04172.x
Protective effect of eotaxin-2 inhibition in adjuvant-induced arthritis
Abstract
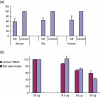
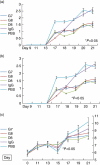
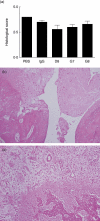
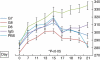
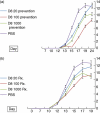
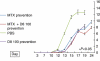
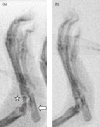
Eotaxin-2 is a potent chemoattractant for eosinophils, basophils and T helper type 2 (Th2) lymphocytes. The eotaxin-2/CCL24 receptor CCR3 is expressed in human brain, skin, endothelium and macrophages. The aim of the current study was to evaluate the protective effect of a monoclonal anti-eotaxin-2 antibody on the development of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats (AIA). Adjuvant arthritis was induced in Lewis rats by intradermal injection of incomplete Freund's adjuvant +Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Rats were treated by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection with three monoclonal antibodies against eotaxin-2 (G7, G8, D8) three times per week. Controls were treated with total mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG), methotrexate (MTX) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Arthritis severity was evaluated by measuring ankle swelling, arthritic score, whole animal mobility and body weight. Sample joints were obtained for pathological evaluation and postmortem X-ray of ankle joints was performed to document erosions. Significant inhibition of arthritis was observed in rats treated with anti-eotaxin-2 antibodies compared to those treated with immunoglobulin or PBS. Inhibition was manifest in ankle diameter, arthritic score and mobility score. The antibody marked D8 showed the greatest efficacy. The effect was observed both in animals treated before the appearance of arthritis and in those where treatment was begun after development of joint inflammation. Combined treatment with D8 and MTX caused additional protection. Significant reduction of inflammation in D8-treated animals was also demonstrated in pathological and X-ray examinations. Inhibition of eotaxin-2 by monoclonal antibodies has a significant protective effect in adjuvant arthritis. These results may introduce a novel therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis and additional inflammatory joint disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-feruloylserotonin in preventive combination therapy with methotrexate reduced inflammation in adjuvant arthritis.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;28(6):616-26. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12085. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24920394
-
Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis.Molecules. 2017 Nov 6;22(11):1911. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111911. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29113115 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the effect of andrographolide and methotrexate combined therapy in complete Freund's adjuvant induced arthritis with reduced hepatotoxicity.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:637-645. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29990853
-
Suppression and augmentation of rat adjuvant arthritis with monoclonal anti-interferon-gamma antibody.Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Nov;78(2):245-9. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989. PMID: 12412757 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Ramucirumab and methotrexate co-therapy in rheumatoid arthritis experimental model: Involvement of angiogenic and immunomodulatory signaling.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 1;380:114702. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114702. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31398424
Cited by
-
Elevated Levels of Eotaxin-2 in Serum of Fibromyalgia Patients.Pain Res Manag. 2018 May 13;2018:7257681. doi: 10.1155/2018/7257681. eCollection 2018. Pain Res Manag. 2018. PMID: 29861805 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-rheumatoid Activity of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Endophytic Chaetomium globosum.Front Microbiol. 2016 Sep 20;7:1477. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01477. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27703452 Free PMC article.
-
Eotaxin-2 increased toll-like receptor 4 expression in endothelial cells in vitro and exacerbates high-cholesterol diet-induced atherogenesis in vivo.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Dec 15;8(12):5338-5353. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 28078007 Free PMC article.
-
Repercussions of adjuvant-induced arthritis on body composition, soleus muscle, and heart muscle of rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020 Mar 2;53(3):e8969. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198969. eCollection 2020. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 32130291 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokines and chemokine receptors as promising targets in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 13;14:1100869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1100869. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36860872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61. - PubMed
-
- Arend WP. Physiology of cytokine pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;45:101–6. - PubMed
-
- Zlotnik A. Chemokines and cancer. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:2026–9. - PubMed
-
- Viola A, Luster AD. Chemokines and their receptors: drug targets in immunity and inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;48:171–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

