Okadaic acid induces tau phosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells in an estrogen-preventable manner
- PMID: 20457142
- PMCID: PMC2913890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.04.074
Okadaic acid induces tau phosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells in an estrogen-preventable manner
Abstract
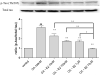
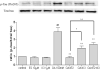
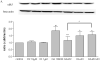
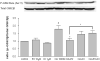
One of the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), which are composed of abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau, but the mechanism of tau hyperphosphorylation in AD is still unclear. To investigate the effects of estrogens on tau phosphorylation, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with okadaic acid (OA), a serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor, to induce tau phosphorylation and the effects of estrogen were observed by co-treatment with 17beta-estradiol (E2). We found that OA induced in vitro tau hyperphosphorylation, which was prevented by E2 in a dose-dependent manner. This effect of E2 was partially blocked by an estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist, ICI 182,780. In addition to tau hyperphosphorylation, inhibition of serine/threonine phosphorylation induced upregulation of cdk5 levels, which was attenuated by E2 in a manner that was counteracted by ICI 182,780. Our results show that cdk5 is involved in OA-induced tau hyperphosphorylation, and estrogens ameliorate the tau hyperphosphorylation, which may be mediated in part by ER.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A overrides tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 inhibition and results in tau hyperphosphorylation in the hippocampus of starved mouse.J Biol Chem. 2001 Sep 7;276(36):34298-306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102780200. Epub 2001 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11441005
-
Estradiol prevents neural tau hyperphosphorylation characteristic of Alzheimer's disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1052:210-24. doi: 10.1196/annals.1347.016. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16024764
-
Effects of PTEN inhibition on regulation of tau phosphorylation in an okadaic acid-induced neurodegeneration model.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012 Oct;30(6):411-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22906543
-
Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells treated with okadaic acid express phosphorylated high molecular weight tau-immunoreactive protein species.J Neurosci Methods. 2019 May 1;319:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.09.030. Epub 2018 Sep 29. J Neurosci Methods. 2019. PMID: 30278184 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein phosphatase-2A and -1 in the regulation of GSK-3, cdk5 and cdc2 and the phosphorylation of tau in rat forebrain.FEBS Lett. 2000 Nov 17;485(1):87-93. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02203-1. FEBS Lett. 2000. PMID: 11086171
Cited by
-
Spontaneous and induced nontransgenic animal models of AD: modeling AD using combinatorial approach.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2013 Jun;28(4):318-26. doi: 10.1177/1533317513488914. Epub 2013 May 17. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2013. PMID: 23687185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxin-Induced Experimental Models of Learning and Memory Impairment.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 1;17(9):1447. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091447. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27598124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish as a model organism for neurodegenerative disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 13;15:940484. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.940484. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36311026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PINCH in the cellular stress response to tau-hyperphosphorylation.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058232. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554879 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of p-Tau Differentiated Cell Model of Alzheimer's Disease to Screen Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 26;23(23):14794. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314794. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso AC, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Alzheimer’s disease hyperphosphorylated tau sequesters normal tau into tangles of filaments and disassembles microtubules. Nat Med. 1996;2:783–787. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-de-la-Rosa M, Silva I, Nilsen J, Perez MM, Garcia-Segura LM, Avila J, Naftolin F. Estradiol prevents neural tau hyperphosphorylation characteristic of alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1052:210–224. - PubMed
-
- Arendt T, Holzer M, Bruckner MK, Janke C, Gartner U. The use of okadaic acid in vivo and the induction of molecular changes typical for alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience. 1998;85:1337–1340. - PubMed
-
- Arias C, Sharma N, Davies P, Shafit-Zagardo B. Okadaic acid induces early changes in microtubule-associated protein 2 and tau phosphorylation prior to neurodegeneration in cultured cortical neurons. J Neurochem. 1993;61:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Avila J, Lucas JJ, Perez M, Hernandez F. Role of tau protein in both physiological and pathological conditions. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:361–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

