Potent hyperglycemic and hyperinsulinemic effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone microinjected into the rostroventrolateral medulla and abnormal responses in type 2 diabetic rats
- PMID: 20457219
- PMCID: PMC3896326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.05.008
Potent hyperglycemic and hyperinsulinemic effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone microinjected into the rostroventrolateral medulla and abnormal responses in type 2 diabetic rats
Abstract
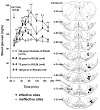
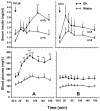
We identified ventrolateral medullary nuclei in which thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) regulates glucose metabolism by modulating autonomic activity. Immunolabeling revealed dense prepro-TRH-containing fibers innervating the rostroventrolateral medulla (RVLM) and nucleus ambiguus (Amb), which contain, respectively, pre-sympathetic motor neurons and vagal motor neurons. In anesthetized Wistar rats, microinjection of the stable TRH analog RX77368 (38-150 pmol) into the RVLM dose-dependently and site-specifically induced hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. At 150 pmol, blood glucose reached a peak of 180+/-18 mg% and insulin increased 4-fold. The strongest hyperglycemic effect was induced when RX77368 was microinjected into C1 area containing adrenalin cells. Spinal cord transection at cervical-7 abolished the hyperglycemia induced by RVLM RX77368, but not the hyperinsulinemic effect. Bilateral vagotomy prevented the rise in insulin, resulting in a prolonged hyperglycemic response. The hyperglycemic and hyperinsulinemic effects of the TRH analog in the RVLM was peptide specific, since angiotensin II or a substance P analog at the same dose had weak or no effects. Microinjection of RX77368 into the Amb stimulated insulin secretion without influencing glucose levels. In conscious type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats, intracisternal injection of RX77368 induced a remarkably amplified hyperglycemic effect with suppressed insulin response compared to Wistar rats. RX77368 microinjected into the RVLM of anesthetized GK rats induced a significantly potentiated hyperglycemic response and an impaired insulin response, compared to Wistar rats. These results indicate that the RVLM is a site at which TRH induces sympathetically-mediated hyperglycemia and vagally-mediated hyperinsulinemia, whereas the Amb is mainly a vagal activating site for TRH. Hyperinsulinemia induced by TRH in the RVLM is not secondary to the hyperglycemic response. The potentiated hyperglycemic and suppressed hyperinsulinemic responses in diabetic GK rats indicate that an unbalanced "sympathetic-over-vagal" activation by TRH in brainstem RVLM contributes to the pathophysiology of impaired glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetes.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



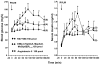


References
-
- Ahren B. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion--implications for health and disease. Diabetologia. 2000;43:393–410. - PubMed
-
- Allen AM, MacGregor DP, McKinley MJ, Mendelsohn FA. Angiotensin II receptors in the human brain. Regul Pept. 1999;79:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Allen AM, O’Callaghan EL, Chen D, Bassi JK. Central Neural Regulation of Cardiovascular Function by Angiotensin: A Focus on the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla. Neuroendocrinology. 2009;89:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Ao Y, Go VL, Toy N, Li T, Wang Y, Song MK, Reeve JRJ, Liu Y, Yang H. Brainstem Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Regulates Food Intake through Vagal-Dependent Cholinergic Stimulation of Ghrelin Secretion. Endocrinology. 2006;147:6004–6010. - PubMed
-
- Ao Y, Toy N, Song MK, Go VL, Yang H. Altered glucose and insulin responses to brain medullary thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-induced autonomic activation in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5425–5432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

