Lapatinib in combination with radiation diminishes tumor regrowth in HER2+ and basal-like/EGFR+ breast tumor xenografts
- PMID: 20457354
- PMCID: PMC2976524
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.12.063
Lapatinib in combination with radiation diminishes tumor regrowth in HER2+ and basal-like/EGFR+ breast tumor xenografts
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether lapatinib, a dual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/HER2 kinase inhibitor, can radiosensitize EGFR+ or HER2+ breast cancer xenografts.
Methods and materials: Mice bearing xenografts of basal-like/EGFR+ SUM149 and HER2+ SUM225 breast cancer cells were treated with lapatinib and fractionated radiotherapy and tumor growth inhibition correlated with alterations in ERK1 and AKT activation by immunohistochemistry.
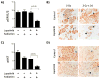
Results: Basal-like/EGFR+ SUM149 breast cancer tumors were completely resistant to treatment with lapatinib alone but highly growth impaired with lapatinib plus radiotherapy, exhibiting an enhancement ratio average of 2.75 and a fractional tumor product ratio average of 2.20 during the study period. In contrast, HER2+ SUM225 breast cancer tumors were highly responsive to treatment with lapatinib alone and yielded a relatively lower enhancement ratio average of 1.25 during the study period with lapatinib plus radiotherapy. Durable tumor control in the HER2+ SUM225 model was more effective with the combination treatment than either lapatinib or radiotherapy alone. Immunohistochemical analyses demonstrated that radiosensitization by lapatinib correlated with ERK1/2 inhibition in the EGFR+ SUM149 model and with AKT inhibition in the HER2+ SUM225 model.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that lapatinib combined with fractionated radiotherapy may be useful against EGFR+ and HER2+ breast cancers and that inhibition of downstream signaling to ERK1/2 and AKT correlates with sensitization in EGFR+ and HER2+ cells, respectively.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none.
Figures

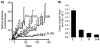
Similar articles
-
Effects of the EGFR/HER2 kinase inhibitor GW572016 on EGFR- and HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell line proliferation, radiosensitization, and resistance.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Feb 1;58(2):344-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.046. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14751502
-
Mechanism of lapatinib-mediated radiosensitization of breast cancer cells is primarily by inhibition of the Raf>MEK>ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade and radiosensitization of lapatinib-resistant cells restored by direct inhibition of MEK.Radiother Oncol. 2009 Dec;93(3):639-44. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Radiother Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19853943 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Feb 1;16(3):912-23. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1324. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20103665 Free PMC article.
-
Lapatinib: a small-molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinases used in the treatment of breast cancer.Clin Ther. 2009;31 Pt 2:2332-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.11.029. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 20110044 Review.
-
Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase activity.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2007 Feb;7(2):257-68. doi: 10.1517/14712598.7.2.257. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17250463 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of Modern Radiotherapy and New Targeted Treatments for Breast Cancer Management.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 18;13(24):6358. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246358. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating the Radiation Response for Improved Outcomes in Breast Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2021 Jan 25;5:PO.20.00297. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00297. eCollection 2021. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34250414 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Strategizing the clone wars: pharmacological control of cellular sensitivity to radiation.Mol Interv. 2010 Dec;10(6):341-53. doi: 10.1124/mi.10.6.3. Mol Interv. 2010. PMID: 21263160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic antitumor effect between gefitinib and fractionated irradiation in anaplastic oligodendrogliomas cannot be predicted by the Egfr signaling activity.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 18;8(7):e68333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068333. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874590 Free PMC article.
-
Co-inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 enhances radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2013 Jun 19;13:297. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-297. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23777562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, et al. The triple negative paradox: Primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–2334. - PubMed
-
- Fadare O, Tavassoli FA. Clinical and pathologic aspects of basal-like breast cancers. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Karasawa K, Katsui K, Seki K, et al. Radiotherapy with concurrent docetaxel for advanced and recurrent breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2003;10:268–274. - PubMed
-
- Suh WW, Schott AF, Hayman JA, et al. A phase I dose escalation trial of gemcitabine with radiotherapy for breast cancer in the treatment of unresectable chest wall recurrences. Breast J. 2004;10:204–210. - PubMed
-
- Tepper JE, Sartor CI. Radiation therapy and biologics: A ripe opportunity? Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2006;3:463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

