NF-kappaB in the immune response of Drosophila
- PMID: 20457557
- PMCID: PMC2882123
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000232
NF-kappaB in the immune response of Drosophila
Abstract
The nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathways play a major role in Drosophila host defense. Two recognition and signaling cascades control this immune response. The Toll pathway is activated by Gram-positive bacteria and by fungi, whereas the immune deficiency (Imd) pathway responds to Gram-negative bacterial infection. The basic mechanisms of recognition of these various types of microbial infections by the adult fly are now globally understood. Even though some elements are missing in the intracellular pathways, numerous proteins and interactions have been identified. In this article, we present a general picture of the immune functions of NF-kappaB in Drosophila with all the partners involved in recognition and in the signaling cascades.
Figures
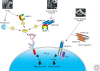


References
-
- Aggarwal K, Silverman N 2008. Positive and negative regulation of the Drosophila immune response. BMB Rep 41:267–277 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS Jr 1996. The NF-κ B and I κ B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–83 - PubMed
-
- Belvin MP, Jin Y, Anderson KV 1995. Cactus protein degradation mediates Drosophila dorsal-ventral signaling. Genes Dev 9:783–793 - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A, Stein D, Geisler R, Hagenmaier S, Schmid B, Fernandez N, Schnell B, Nüsslein-Volhard C 1996. A gradient of cytoplasmic Cactus degradation establishes the nuclear localization gradient of the dorsal morphogen in Drosophila. Mech Dev 60:109–123 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
