Adherens junction: molecular architecture and regulation
- PMID: 20457565
- PMCID: PMC2882120
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002899
Adherens junction: molecular architecture and regulation
Abstract
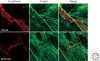
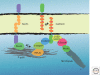
The adherens junction (AJ) is an element of the cell-cell junction in which cadherin receptors bridge the neighboring plasma membranes via their homophilic interactions. Cadherins associate with cytoplasmic proteins, called catenins, which in turn bind to cytoskeletal components, such as actin filaments and microtubules. These molecular complexes further interact with other proteins, including signaling molecules, rendering the AJs into highly dynamic and regulatable structures. The AJs of such nature contribute to the physical linking of cells, as well as to the regulation of cell-cell contacts, which is essential for morphogenesis and remodeling of tissues and organs. Thus, elucidating the molecular architecture of the AJs and their regulatory mechanisms are crucial for understanding how the multicellular system is organized.
Figures
References
-
- Abe K, Chisaka O, Van Roy F, Takeichi M 2004. Stability of dendritic spines and synaptic contacts is controlled by α N-catenin. Nat Neurosci 7:357–363 - PubMed
-
- Afonso C, Henrique D 2006. PAR3 acts as a molecular organizer to define the apical domain of chick neuroepithelial cells. J Cell Sci 119:4293–4304 - PubMed
-
- Bertet C, Sulak L, Lecuit T 2004. Myosin-dependent junction remodelling controls planar cell intercalation and axis elongation. Nature 429:667–671 - PubMed
-
- Blankenship JT, Backovic ST, Sanny JS, Weitz O, Zallen JA 2006. Multicellular rosette formation links planar cell polarity to tissue morphogenesis. Dev Cell 11:459–470 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
