Allele frequency-based and polymorphism-versus-divergence indices of balancing selection in a new filtered set of polymorphic genes in Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 20457586
- PMCID: PMC2944029
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msq119
Allele frequency-based and polymorphism-versus-divergence indices of balancing selection in a new filtered set of polymorphic genes in Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
Signatures of balancing selection operating on specific gene loci in endemic pathogens can identify candidate targets of naturally acquired immunity. In malaria parasites, several leading vaccine candidates convincingly show such signatures when subjected to several tests of neutrality, but the discovery of new targets affected by selection to a similar extent has been slow. A small minority of all genes are under such selection, as indicated by a recent study of 26 Plasmodium falciparum merozoite-stage genes that were not previously prioritized as vaccine candidates, of which only one (locus PF10_0348) showed a strong signature. Therefore, to focus discovery efforts on genes that are polymorphic, we scanned all available shotgun genome sequence data from laboratory lines of P. falciparum and chose six loci with more than five single nucleotide polymorphisms per kilobase (including PF10_0348) for in-depth frequency-based analyses in a Kenyan population (allele sample sizes >50 for each locus) and comparison of Hudson-Kreitman-Aguade (HKA) ratios of population diversity (π) to interspecific divergence (K) from the chimpanzee parasite Plasmodium reichenowi. Three of these (the msp3/6-like genes PF10_0348 and PF10_0355 and the surf(4.1) gene PFD1160w) showed exceptionally high positive values of Tajima's D and Fu and Li's F indices and have the highest HKA ratios, indicating that they are under balancing selection and should be prioritized for studies of their protein products as candidate targets of immunity. Combined with earlier results, there is now strong evidence that high HKA ratio (as well as the frequency-independent ratio of Watterson's /K) is predictive of high values of Tajima's D. Thus, the former offers value for use in genome-wide screening when numbers of genome sequences within a species are low or in combination with Tajima's D as a 2D test on large population genomic samples.
Figures

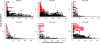
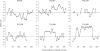
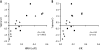
Similar articles
-
Prospective identification of malaria parasite genes under balancing selection.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005568. Epub 2009 May 15. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19440377 Free PMC article.
-
Population genomic scan for candidate signatures of balancing selection to guide antigen characterization in malaria parasites.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1002992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002992. Epub 2012 Nov 1. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23133397 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of selection on the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in West African populations of differing infection endemicity.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 Jun;31(6):1490-9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu106. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24644299 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting signatures of balancing selection to identify targets of anti-parasite immunity.Trends Parasitol. 2010 Jul;26(7):363-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2010.04.002. Epub 2010 May 11. Trends Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20466591 Review.
-
Genetic diversity and population history of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax.Parassitologia. 2006 Dec;48(4):561-6. Parassitologia. 2006. PMID: 17688177 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Antibodies in children with malaria to PfEMP1, RIFIN and SURFIN expressed at the Plasmodium falciparum parasitized red blood cell surface.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 19;8(1):3262. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21026-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29459776 Free PMC article.
-
Selections, frameshift mutations, and copy number variation detected on the surf 4.1 gene in the western Kenyan Plasmodium falciparum population.Malar J. 2017 Mar 2;16(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1743-x. Malar J. 2017. PMID: 28253868 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation sequencing to detect variation in the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012 May;86(5):775-81. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.11-0478. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012. PMID: 22556073 Free PMC article.
-
Fifteen years of genomewide scans for selection: trends, lessons and unaddressed genetic sources of complication.Mol Ecol. 2016 Jan;25(1):5-23. doi: 10.1111/mec.13339. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Mol Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26224644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population genetic analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum 6-cys protein Pf38 in Papua New Guinea reveals domain-specific balancing selection.Malar J. 2011 May 14;10:126. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-126. Malar J. 2011. PMID: 21569602 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

