The KRAS promoter responds to Myc-associated zinc finger and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 proteins, which recognize a critical quadruplex-forming GA-element
- PMID: 20457603
- PMCID: PMC2903372
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101923
The KRAS promoter responds to Myc-associated zinc finger and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 proteins, which recognize a critical quadruplex-forming GA-element
Abstract
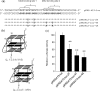
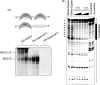
The murine KRAS promoter contains a G-rich nuclease hypersensitive element (GA-element) upstream of the transcription start site that is essential for transcription. Pulldown and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrate that this GA-element is bound by the Myc-associated zinc finger (MAZ) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) proteins. These proteins are crucial for transcription, because when they are knocked down by short hairpin RNA, transcription is down-regulated. This is also the case when the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation activity of PARP-1 is inhibited by 3,4-dihydro-5-[4-(1-piperidinyl) butoxyl]-1(2H) isoquinolinone. We found that MAZ specifically binds to the duplex and quadruplex conformations of the GA-element, whereas PARP-1 shows specificity only for the G-quadruplex. On the basis of fluorescence resonance energy transfer melting and polymerase stop assays we saw that MAZ stabilizes the KRAS quadruplex. When the capacity of folding in the GA-element is abrogated by specific G --> T or G --> A point mutations, KRAS transcription is down-regulated. Conversely, guanidine-modified phthalocyanines, which specifically interact with and stabilize the KRAS G-quadruplex, push the promoter activity up to more than double. Collectively, our data support a transcription mechanism for murine KRAS that involves MAZ, PARP-1 and duplex-quadruplex conformational changes in the promoter GA-element.
Figures







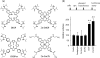
Similar articles
-
The guanine-quadruplex structure in the human c-myc gene's promoter is converted into B-DNA form by the human poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042690. Epub 2012 Aug 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22880082 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution three-dimensional NMR structure of the KRAS proto-oncogene promoter reveals key features of a G-quadruplex involved in transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2017 May 12;292(19):8082-8091. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.781906. Epub 2017 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28330874 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Poly [ADP-ribose] Polymerase 1 in Activating the Kirsten ras (KRAS) Gene in Response to Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 28;21(17):6237. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176237. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32872305 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of hnRNP A1 in activating KRAS transcription in pancreatic cancer cells: A molecular mechanism involving G4 DNA.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt B):1389-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.11.031. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27888145 Review.
-
Non-duplex G-Quadruplex Structures Emerge as Mediators of Epigenetic Modifications.Trends Genet. 2019 Feb;35(2):129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 30527765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The DNA secondary structures at telomeres and genome instability.Cell Biosci. 2020 Mar 26;10:47. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00409-z. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32257105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Non-continuum Nature of Eukaryotic Transcriptional Regulation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1371:11-32. doi: 10.1007/5584_2021_618. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 33616894 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription regulation of CDKN1A (p21/CIP1/WAF1) by TRF2 is epigenetically controlled through the REST repressor complex.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 14;7(1):11541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11177-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28912501 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the transcription factor MAZ as a regulator of erythropoiesis.Blood Adv. 2021 Aug 10;5(15):3002-3015. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004609. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 34351390 Free PMC article.
-
G-Quadruplex-Binding Proteins: Promising Targets for Drug Design.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 29;12(5):648. doi: 10.3390/biom12050648. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

