Roles of fragile X mental retardation protein in dopaminergic stimulation-induced synapse-associated protein synthesis and subsequent alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA) receptor internalization
- PMID: 20457613
- PMCID: PMC2898437
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.116293
Roles of fragile X mental retardation protein in dopaminergic stimulation-induced synapse-associated protein synthesis and subsequent alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA) receptor internalization
Abstract
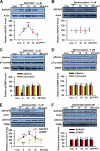
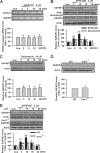
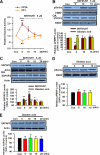
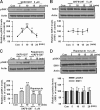
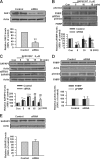
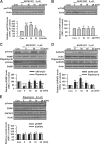
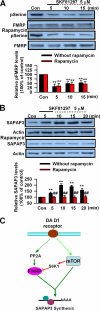
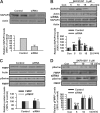
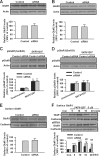
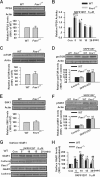
Fragile X syndrome, the most common form of inherited mental retardation, is caused by the absence of the RNA-binding protein fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP). FMRP regulates local protein synthesis in dendritic spines. Dopamine (DA) is involved in the modulation of synaptic plasticity. Activation of DA receptors can regulate higher brain functions in a protein synthesis-dependent manner. Our recent study has shown that FMRP acts as a key messenger for DA modulation in forebrain neurons. Here, we demonstrate that FMRP is critical for DA D1 receptor-mediated synthesis of synapse-associated protein 90/PSD-95-associated protein 3 (SAPAP3) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC). DA D1 receptor stimulation induced dynamic changes of FMRP phosphorylation. The changes in FMRP phosphorylation temporally correspond with the expression of SAPAP3 after D1 receptor stimulation. Protein phosphatase 2A, ribosomal protein S6 kinase, and mammalian target of rapamycin are the key signaling molecules for FMRP linking DA D1 receptors to SAPAP3. Knockdown of SAPAP3 did not affect surface expression of alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA) GluR1 receptors induced by D1 receptor activation but impaired their subsequent internalization in cultured PFC neurons; the subsequent internalization of GluR1 was also impaired in Fmr1 knock-out PFC neurons, suggesting that FMRP may be involved in subsequent internalization of GluR1 through regulating the abundance of SAPAP3 after DA D1 receptor stimulation. Our study thus provides further insights into FMRP involvement in DA modulation and may help to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying impaired learning and memory in fragile X syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Bear M. F., Huber K. M., Warren S. T. (2004) Trends Neurosci. 27, 370–377 - PubMed
-
- Belmonte M. K., Bourgeron T. (2006) Nat. Neurosci. 9, 1221–1225 - PubMed
-
- Feng Y., Zhang F., Lokey L. K., Chastain J. L., Lakkis L., Eberhart D., Warren S. T. (1995) Science 268, 731–734 - PubMed
-
- Terracciano A., Chiurazzi P., Neri G. (2005) Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 137c, 32–37 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

