Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation
- PMID: 20457754
- PMCID: PMC2943593
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq347
Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation
Abstract
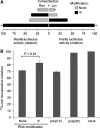
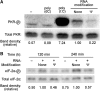
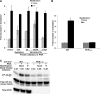
Previous studies have shown that the translation level of in vitro transcribed messenger RNA (mRNA) is enhanced when its uridines are replaced with pseudouridines; however, the reason for this enhancement has not been identified. Here, we demonstrate that in vitro transcripts containing uridine activate RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR), which then phosphorylates translation initiation factor 2-alpha (eIF-2α), and inhibits translation. In contrast, in vitro transcribed mRNAs containing pseudouridine activate PKR to a lesser degree, and translation of pseudouridine-containing mRNAs is not repressed. RNA pull-down assays demonstrate that mRNA containing uridine is bound by PKR more efficiently than mRNA with pseudouridine. Finally, the role of PKR is validated by showing that pseudouridine- and uridine-containing RNAs were translated equally in PKR knockout cells. These results indicate that the enhanced translation of mRNAs containing pseudouridine, compared to those containing uridine, is mediated by decreased activation of PKR.
Figures

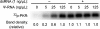

References
-
- Weissman D, Ni H, Scales D, Dude A, Capodici J, McGibney K, Abdool A, Isaacs SN, Cannon G, Karikó K. HIV gag mRNA transfection of dendritic cells (DC) delivers encoded antigen to MHC class I and II molecules, causes DC maturation, and induces a potent human in vitro primary immune response. J. Immunol. 2000;165:4710–4717. - PubMed
-
- Nienhuis AW, Dunbar CE, Sorrentino BP. Genotoxicity of retroviral integration in hematopoietic cells. Mol. Ther. 2006;13:1031–1049. - PubMed
-
- Donsante A, Miller DG, Li Y, Vogler C, Brunt EM, Russell DW, Sands MS. AAV vector integration sites in mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. Science. 2007;317:477. - PubMed
-
- KarikóK, Buckstein M, Ni H, Weissman D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity. 2005;23:165–175. - PubMed
-
- Hornung V, Ellegast J, Kim S, Brzozka K, Jung A, Kato H, Poeck H, Akira S, Conzelmann K.-K, Schlee M, et al. 5′-Triphosphate RNA is the ligand for RIG-I. Science. 2006;314:994–997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

