Sox10 is required for Schwann cell identity and progression beyond the immature Schwann cell stage
- PMID: 20457761
- PMCID: PMC2872908
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200912142
Sox10 is required for Schwann cell identity and progression beyond the immature Schwann cell stage
Abstract
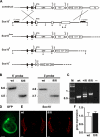
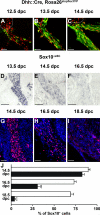
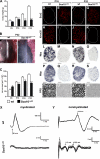
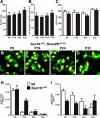
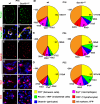
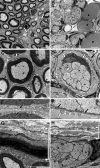
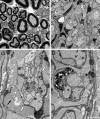
Mutations in the transcription factor SOX10 cause neurocristopathies, including Waardenburg-Hirschsprung syndrome and peripheral neuropathies in humans. This is partly attributed to a requirement for Sox10 in early neural crest for survival, maintenance of pluripotency, and specification to several cell lineages, including peripheral glia. As a consequence, peripheral glia are absent in Sox10-deficient mice. Intriguingly, Sox10 continues to be expressed in these cells after specification. To analyze glial functions after specification, we specifically deleted Sox10 in immature Schwann cells by conditional mutagenesis. Mutant mice died from peripheral neuropathy before the seventh postnatal week. Nerve alterations included a thinned perineurial sheath, increased lipid and collagen deposition, and a dramatically altered cellular composition. Nerve conduction was also grossly aberrant, and neither myelinating nor nonmyelinating Schwann cells formed. Instead, axons of different sizes remained unsorted in large bundles. Schwann cells failed to develop beyond the immature stage and were unable to maintain identity. Thus, our study identifies a novel cause for peripheral neuropathies in patients with SOX10 mutations.
Figures

References
-
- Barbaria E.M., Kohl B., Buhren B.A., Hasenpusch-Theil K., Kruse F., Küry P., Martini R., Müller H.W. 2009. The alpha-chemokine CXCL14 is up-regulated in the sciatic nerve of a mouse model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A and alters myelin gene expression in cultured Schwann cells. Neurobiol. Dis. 33:448–458 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.11.014 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benninger Y., Thurnherr T., Pereira J.A., Krause S., Wu X., Chrostek-Grashoff A., Herzog D., Nave K.A., Franklin R.J., Meijer D., et al. 2007. Essential and distinct roles for cdc42 and rac1 in the regulation of Schwann cell biology during peripheral nervous system development. J. Cell Biol. 177:1051–1061 10.1083/jcb.200610108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berman M.E., Xie Y., Muller W.A. 1996. Roles of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1, CD31) in natural killer cell transendothelial migration and beta 2 integrin activation. J. Immunol. 156:1515–1524 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

