The acidic A-domain of Arabidopsis TOC159 occurs as a hyperphosphorylated protein
- PMID: 20457805
- PMCID: PMC2899928
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.110.158048
The acidic A-domain of Arabidopsis TOC159 occurs as a hyperphosphorylated protein
Abstract
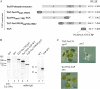
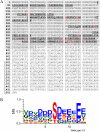
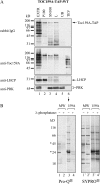
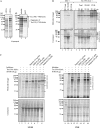
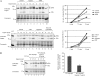
The translocon at the outer membrane of the chloroplast assists the import of a large class of preproteins with amino-terminal transit sequences. The preprotein receptors Toc159 and Toc33 in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) are specific for the accumulation of abundant photosynthetic proteins. The receptors are homologous GTPases known to be regulated by phosphorylation within their GTP-binding domains. In addition to the central GTP-binding domain, Toc159 has an acidic N-terminal domain (A-domain) and a C-terminal membrane-anchoring domain (M-domain). The A-domain of Toc159 is dispensable for its in vivo activity in Arabidopsis and prone to degradation in pea (Pisum sativum). Therefore, it has been suggested to have a regulatory function. Here, we show that in Arabidopsis, the A-domain is not simply degraded but that it accumulates as a soluble, phosphorylated protein separated from Toc159. However, the physiological relevance of this process is unclear. The data show that the A-domain of Toc159 as well as those of its homologs Toc132 and Toc120 are targets of a casein kinase 2-like activity.
Figures



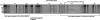
References
-
- Aronsson H, Combe J, Patel R, Jarvis P. (2006) In vivo assessment of the significance of phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis chloroplast protein import receptor, atToc33. FEBS Lett 580: 649–655 - PubMed
-
- Bauer J, Chen K, Hiltbunner A, Wehrli E, Eugster M, Schnell D, Kessler F. (2000) The major protein import receptor of plastids is essential for chloroplast biogenesis. Nature 403: 203–207 - PubMed
-
- Blom N, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Gupta R, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S. (2004) Prediction of post-translational glycosylation and phosphorylation of proteins from the amino acid sequence. Proteomics 4: 1633–1649 - PubMed
-
- Bolter B, May T, Soll J. (1998) A protein import receptor in pea chloroplasts, Toc86, is only a proteolytic fragment of a larger polypeptide. FEBS Lett 441: 59–62 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

