Three key subregions contribute to the function of the downstream RNA polymerase II core promoter
- PMID: 20457814
- PMCID: PMC2897566
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00053-10
Three key subregions contribute to the function of the downstream RNA polymerase II core promoter
Abstract
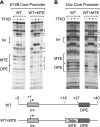
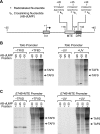
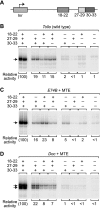
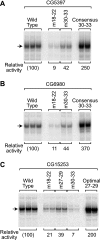
The RNA polymerase II core promoter is a diverse and complex regulatory element. To gain a better understanding of the core promoter, we examined the motif 10 element (MTE), which is located downstream of the transcription start site and acts in conjunction with the initiator (Inr). We found that the MTE promotes the binding of purified TFIID to the core promoter and that the TAF6 and TAF9 subunits of TFIID appear to be in close proximity to the MTE. To identify the specific nucleotides that contribute to MTE activity, we performed a detailed mutational analysis and determined a functional MTE consensus sequence. These studies identified favored as well as disfavored nucleotides and demonstrated the previously unrecognized importance of nucleotides in the subregion of nucleotides 27 to 29 (+27 to + 29 relative to A(+1) in the Inr consensus) for MTE function. Further analysis led to the identification of three downstream subregions (nucleotides 18 to 22, 27 to 29, and 30 to 33) that contribute to core promoter activity. The three binary combinations of these subregions lead to the MTE (nucleotides 18 to 22 and 27 to 29), a downstream core promoter element (nucleotides 27 to 29 and 30 to 33), and a novel "bridge" core promoter motif (nucleotides 18 to 22 and 30 to 33). These studies have thus revealed a tripartite organization of key subregions in the downstream core promoter.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The MTE, a new core promoter element for transcription by RNA polymerase II.Genes Dev. 2004 Jul 1;18(13):1606-17. doi: 10.1101/gad.1193404. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15231738 Free PMC article.
-
A transcription factor IIA-binding site differentially regulates RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription in a promoter context-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 14;292(28):11873-11885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770412. Epub 2017 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28539359 Free PMC article.
-
TAF4 nucleates a core subcomplex of TFIID and mediates activated transcription from a TATA-less promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12347-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605499103. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16895980 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA Polymerase II Core Promoter in Drosophila.Genetics. 2019 May;212(1):13-24. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302021. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31053615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on the RNA polymerase II core promoter.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 Jan-Feb;1(1):40-51. doi: 10.1002/wdev.21. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23801666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human TFIID binds to core promoter DNA in a reorganized structural state.Cell. 2013 Jan 17;152(1-2):120-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.005. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23332750 Free PMC article.
-
Highly redundant function of multiple AT-rich sequences as core promoter elements in the TATA-less RPS5 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(1):59-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq741. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20805245 Free PMC article.
-
TSS seq based core promoter architecture in blood feeding Tsetse fly (Glossina morsitans morsitans) vector of Trypanosomiasis.BMC Genomics. 2015 Sep 22;16(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1921-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26394619 Free PMC article.
-
Critical assessment of computational tools for prokaryotic and eukaryotic promoter prediction.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Mar 10;23(2):bbab551. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab551. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35021193 Free PMC article.
-
Are complex traits underpinned by polygenic molecular traits? A reflection on the complexity of gene expression.Plant Cell Physiol. 2025 May 17;66(4):444-460. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcae140. Plant Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39626022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burke, T. W., and J. T. Kadonaga. 1996. Drosophila TFIID binds to a conserved downstream basal promoter element that is present in many TATA-box-deficient promoters. Genes Dev. 10:711-724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
