A mechanosensitive ion channel regulating cell volume
- PMID: 20457830
- PMCID: PMC2889639
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00503.2009
A mechanosensitive ion channel regulating cell volume
Abstract
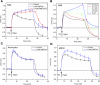
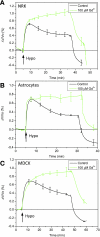
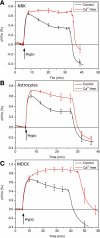
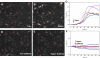
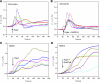
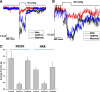
Cells respond to a hyposmotic challenge by swelling and then returning toward the resting volume, a process known as the regulatory volume decrease or RVD. The sensors for this process have been proposed to include cationic mechanosensitive ion channels that are opened by membrane tension. We tested this hypothesis using a microfluidic device to measure cell volume and the peptide GsMTx4, a specific inhibitor of cationic mechanosensitive channels. GsMTx4 had no effect on RVD in primary rat astrocytes or Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells but was able to completely inhibit RVD and the associated Ca(2+) uptake in normal rat kidney (NRK-49F) cells in a dose-dependent manner. Gadolinium (Gd(3+)), a nonspecific blocker of many mechanosensitive channels, inhibited RVD and Ca(2+) uptake in all three cell types, demonstrating the existence of at least two types of volume sensors. Single-channel stretch-activated currents are present in outside-out patches from NRK-49F, MDCK, and astrocytes, and they are reversibly inhibited by GsMTx4. While mechanosensitive channels are involved in volume regulation, their role for volume sensing is specialized. The NRK cells form a stable platform from which to screen drugs that affect volume regulation via mechanosensory channels and as a sensitive system to clone the channel.
Figures
References
-
- Acher R. Water homeostasis in the living: molecular organization, osmoregulatory reflexes and evolution. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 63: 197–218, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Arniges M, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Valverde MA. Swelling-activated Ca2+ entry via TRPV4 channel is defective in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J Biol Chem 279: 54062–54068, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Ateya DA, Sachs F, Gottlieb PA, Besch S, Hua SZ. Volume cytometry: microfluidic sensor for high-throughput screening in real time. Anal Chem 77: 1290–1294, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Becker D, Blase C, Bereiter-Hahn J, Jendrach M. TRPV4 exhibits a functional role in cell-volume regulation. J Cell Sci 118: 2435–2440, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bode F, Sachs F, Franz MR. Tarantula peptide inhibits atrial fibrillation. Nature 409: 35–36, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

